FIG 4.
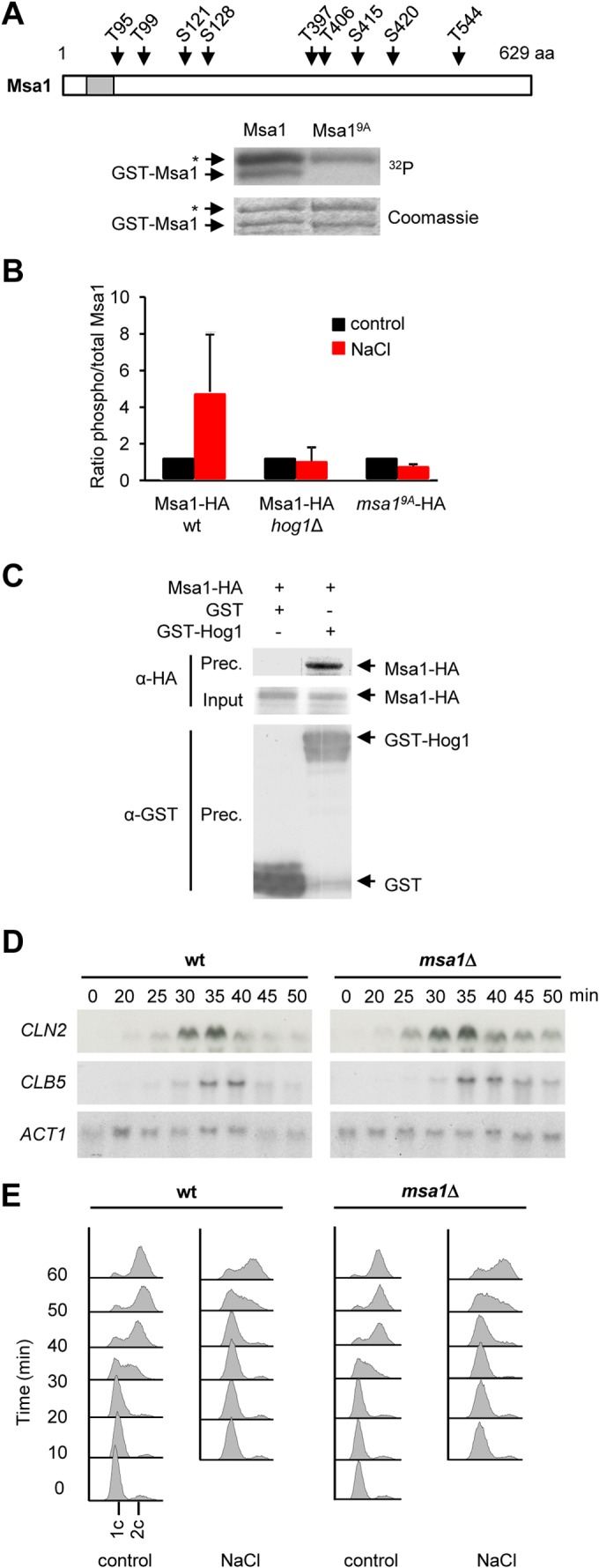
Hog1 targets the Msa1 transcriptional coregulator. (A) Mutation of nine residues in Msa1 abolished Hog1 phosphorylation in vitro. GST-Msa1 or GST-Msa19A was purified from bacteria, subjected to an in vitro kinase assay with activated Hog1, and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 3A. Asterisks indicate bands that correspond to purified GST-Pbs2EE. The location of the mapped residues in the Msa1 protein is shown in the cartoon at top. The gray box denotes a predicted nuclear localization signal. aa, amino acids. (B) Msa1 is phosphorylated by Hog1 in vivo. Wild-type (wt) yeast cells expressing Msa1-HA or msa19A-HA, as well as hog1Δ mutant cells expressing Msa1-HA, were synchronized with α-factor and treated with brief osmotic shock (0.4 M NaCl, 10 min) or left untreated (control). Protein extracts were then immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody. SP/TP phosphorylated proteins were detected with an anti-phosphoserine-threonine antibody (BD Transduction Laboratories). Bars represent the average ratios of phosphorylated to total Msa1 ± the standard deviations from three independent experiments. (C) Hog1 and Msa1 coimmunoprecipitate in vivo. Cells expressing Msa1-HA and either GST-Hog1 or GST alone were stressed with 0.4 M NaCl for 10 min. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-GST antibody. Precipitated proteins (Prec.) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for Msa1 and Hog1 with anti-HA and anti-GST probes, respectively. The input represents 2.5% of the immunoprecipitated protein. (D) Transcription delay of G1 cyclins is not reduced in msa1Δ mutant cells. Wild-type and msa1Δ mutant cells were synchronized in G1 with α-factor and released into 0.4 M NaCl. Samples were taken at the times indicated after release for RNA extraction for Northern blot analysis. CLN2 and CLB5 mRNAs were detected with specific probes. ACT1 was probed as a loading control. (E) DNA replication is delayed independently of Msa1 upon osmostress. Wild-type or msa1Δ mutant cells were synchronized with α-factor and released into control or 0.4 M NaCl medium. Samples were taken every 10 min after release and analyzed for DNA replication by flow cytometry.
