Fig. 2.
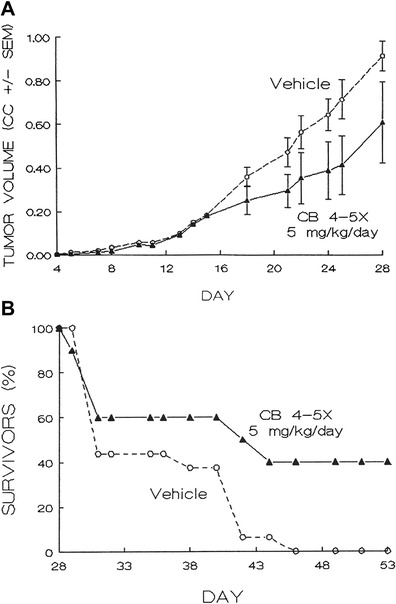
Intravenously administered cytochalasin B against M109 murine lung carcinoma. a Effect of intravenously administered cytochalasin B on growth of intradermal M109 carcinoma nodules. 10 mice received at least 4 injections of CB at 5 mg/kg in 33 % ethanol:0.9 % NaCl solution i.v. on days 1–5 following challenge on day 0 with 2 × 105 M109c cells i.d. 16 Balb/c mice received vehicle i.v. as a control. CC = cm3. The CB-treated group was significantly different from the controls; p < 0.02 for between subject effects, p < 0.05 for time vs. group interactions. Bars reflect SEM of the treatment groups. b Effects of intravenously administered cytochalasin B on survival of Balb/c mice. Both treated and control mice were administered the same concentrations of cytochalasin B or vehicle-only as shown in Fig. 2a. Survival of treated mice (n = 10) was significantly different from controls (n = 16); p < 0.05, as assessed by a Cox-Mantel test
