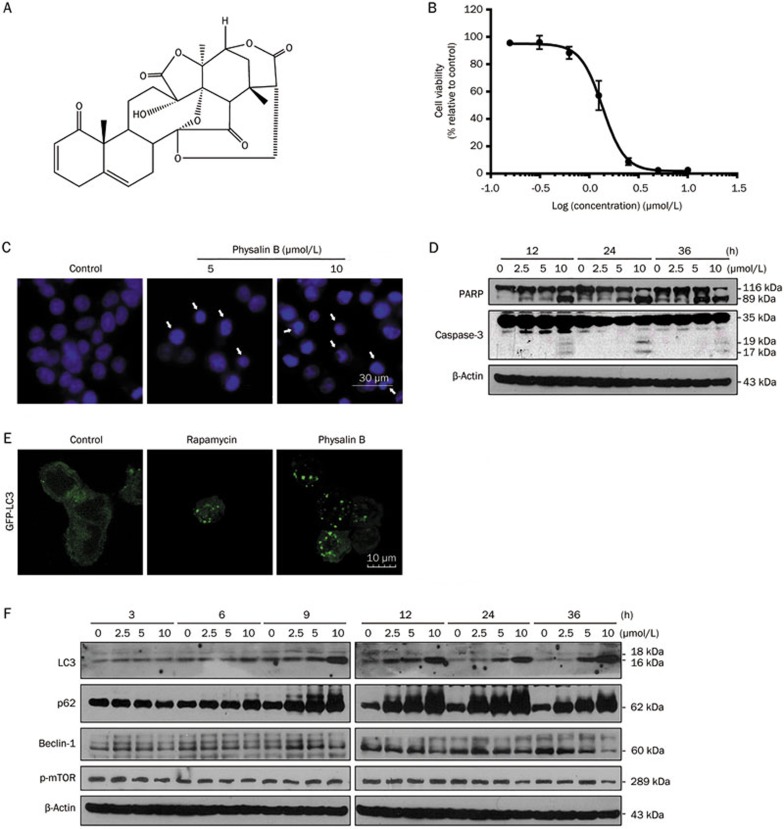
Figure 1.
Physalin B induced apoptosis and an initial stage of autophagy in HCT116 colon cancer cells. (A) The chemical structure of physalin B. (B) Physalin B inhibited HCT116 cell viability. Cells were treated with physalin B at doses ranging from 10 μmol/L to 0.31 μmol/L for 72 h. The cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. IC50 value is expressed as the mean±SEM of four independent experiments. (C) Physalin B induced pyknosis and formation of apoptotic bodies. Cells were treated with 5 and 10 μmol/L physalin B for 24 h and further stained with Hoechst 33342 and observed under microscope. (D) Cells were treated with 2.5, 5, and 10 μmol/L physalin B. Samples were collected at 12, 24, and 36 h, separately. Levels of PARP and caspase-3 were detected using Western blotting assay. (E) Physalin B induced autophagosome formation in GFP-LC3-expressing HCT116 cells. GFP-LC3-expressing HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L physalin B, 0.1% DMSO (negative control) and 5 μmol/L rapamycin (positive control) for 12 h. Autophagosomes were observed under an Olympus Fluoview FV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). (F) Cells were treated with 2.5, 5, and 10 μmol/L physalin B. Samples were collected at 3, 6, 9, 12, 24, and 36 h separately. Levels of LC3, p62, Beclin-1, pSer2448-mTOR, and β-actin were detected using Western blotting assay.