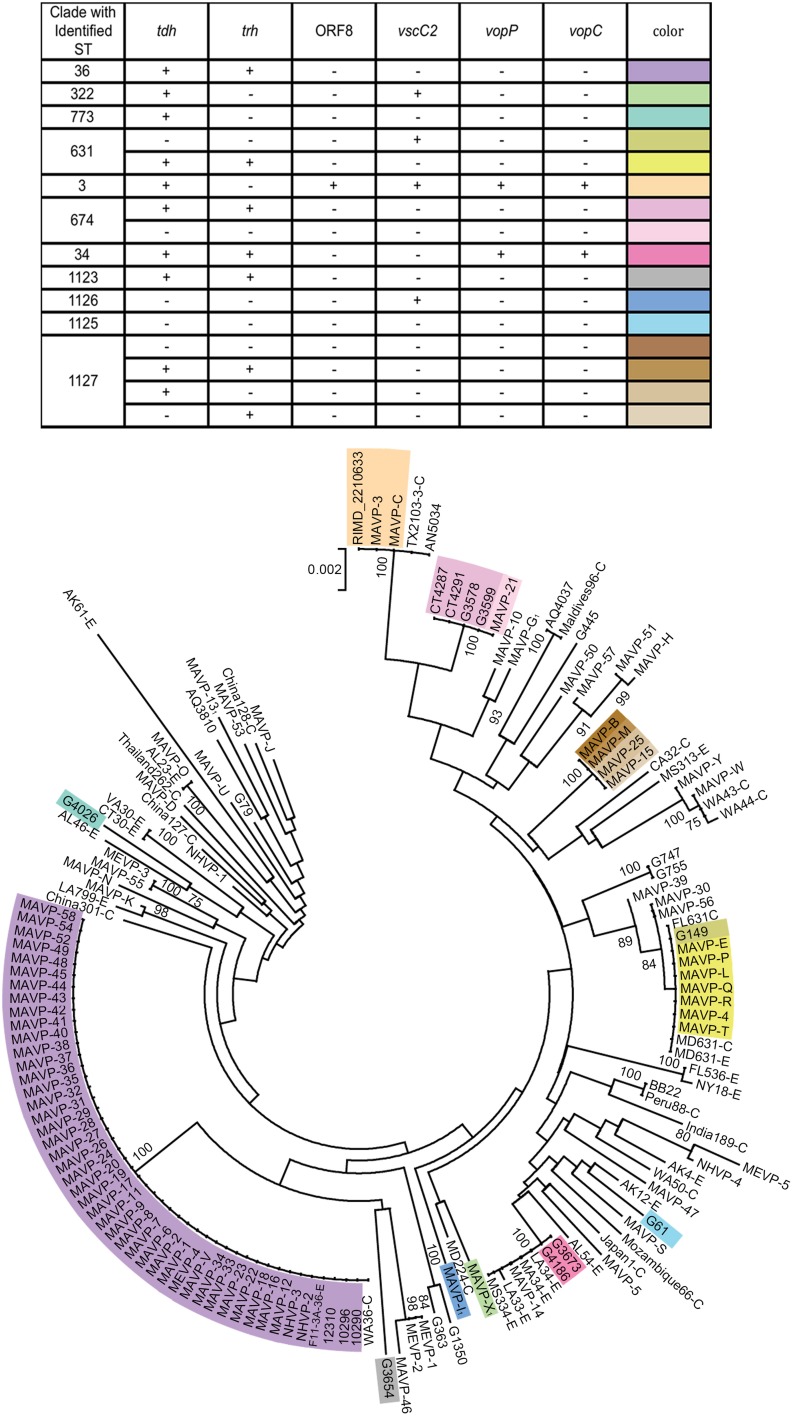
Figure 2.
Population structure of Northeast US clinical, related environmental, and some unique worldwide isolates of V. parahaemolyticus. A consensus neighbor-joining tree was constructed from four concatenated housekeeping gene loci including dnaE, dtdS, pntA, and tnaA sequences by using a Jukes-Cantor model. For ease in distinguishing pertinent information associated with worldwide strains from the MLST database, a single representative strain from several sequence types was identified from among the available strains, and the representative strain identified by geographic location (USA by state, international by country name), sequence type number, and as clinical (C) or environmental (E). Environmental strains from the region included isolates from the Great Bay Estuary (all with prefix G) or Connecticut (CT). For seven strains whose draft or complete genomes are publicly available, the loci were recovered from the available assemblies. Among related strains where the probable sequence type of the strains was determined, unique genotypes are indicated by color provided in the key and overlaid upon the tree. The bar indicates 0.2% divergences, and branches with less than 70% bootstrap support are unlabeled. Several clinical strains, for which one or more housekeeping loci were not successfully amplified and sequenced were excluded from the analysis (MAVP-A, MAVP-F, MAVP-59, MEVP-6). 1Isolates were from wound infections.