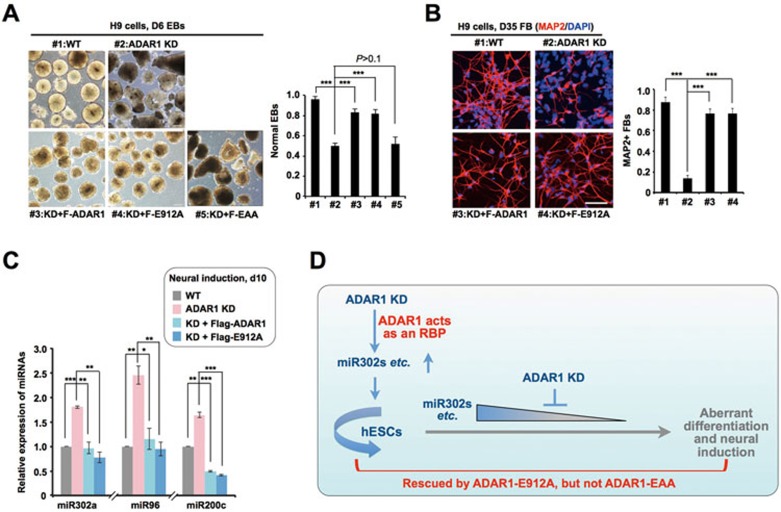
Figure 7.
Catalytically inactive Flag-E912A rescues the retarded neural induction and aberrant miRNA expression upon differentiation in ADAR1 KD H9 cells. (A) Flag-E912A, but not Flag-EAA, could reverse the aberrant EB formation derived from ADAR1 KD H9 cells. Left, representative images of EBs derived from different H9 cell lines. Right, the percentage of morphologically normal EBs derived from different H9 cell lines (n > 200). (B) Flag-E912A restored the repressed neural induction in ADAR1 KD H9 cells. Left, representative images of MAP2+ FB neurons derived from different H9 cell lines. Right, the percentage of MAP2+ cells derived from different H9 cell lines (n > 200). (C) Flag-E912A reversed the upregulation of neural induction repression-related miRNAs in ADAR1 KD H9 cells at d10 upon neural induction, as revealed by RT-qPCR (normalized to U6). (D) A model for ADAR1 regulation in hESC self-renewal and differentiation. ADAR1 inhibits the processing of pri-mi302s and other miRNAs in hESCs upon differentiation by acting as a dsRNA-binding protein. In A, B and C, error bars represent ± SD of triplicate experiments. P values from one-tail t-tests are shown.