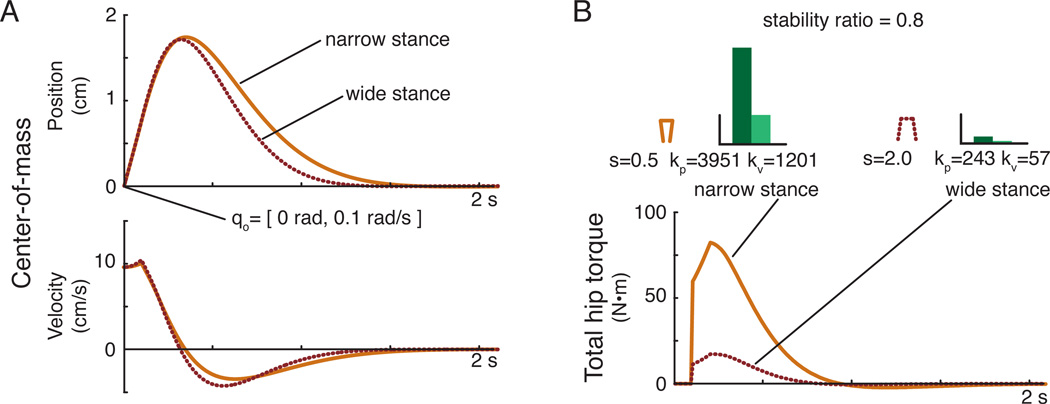
Figure 5.
Simulated center-of-mass position across stance widths using feedback gains that produce the same stability radius. (A) Although feedback gain values differed substantially across stance widths, the resulting center-of-mass motion produced in response to a change in the initial state of the system was similar in narrow (solid) and wide (dotted) stance widths when feedback gains with the same stability radius were used. (B) The resulting torque necessary to generate the center-of-mass response was an order of magnitude smaller for the wide stance compared to the narrow stance.