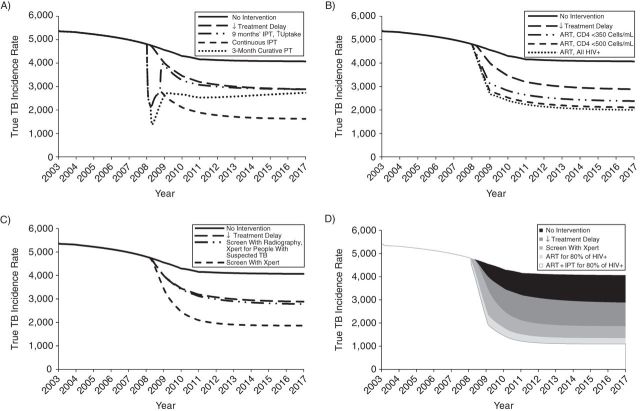
Figure 6.
Impact of different interventions implemented individually (A–C) or in combination (D) predicted for the Thibela TB randomized controlled trial among South African gold miners, 2006–2011. Summary of the predicted impact of different interventions on the number of cases/100,000/year (the true TB incidence rate), after the treatment delay has been reduced. Each panel shows the impact of reduced treatment delay plus in A) preventive treatment, with 1) IPT provided community-wide in an initial round for 9 months of IPT, with coverage at the highest levels seen in Thibela, and 2) IPT provided community-wide in an initial round for 9 months, with coverage at the highest levels seen in Thibela, followed by continuous community-wide IPT with 50% coverage. This is achieved through keeping those who are still on IPT at the end of the initial round on IPT thereafter and providing IPT to 50% of new mining employees, and 3) a single round with a 3-month fully curing regimen provided community-wide (without 9 months of IPT), with coverage at the highest levels seen in Thibela. B) Scale-up of ART, with ART coverage increasing to reach 80% in 2009 in the HIV-positive groups specified in the figure legend; C) improved diagnosis using Xpert MTB/RIF, with 1) radiographs being used to screen at routine medical examinations and for newly employed miners and Xpert MTB/RIF being used to diagnose people with suspected TB, and 2) Xpert MTB/RIF being used to screen and diagnose at routine medical examinations for newly employed miners and on passive presentation; D) combined interventions. Combined impact of introducing reduced treatment delay, screening with Xpert MTB/RIF, ART for 80% of HIV-positive people, and IPT for those on ART. The shaded areas show the incremental impact of adding each intervention, so that the white area reflects the impact of having all interventions in place simultaneously. For the scenario involving Xpert MTB/RIF, Xpert MTB/RIF is used in routine medical examinations, for newly employed miners, and on passive presentation. For both the ART and ART/IPT scenarios, the coverage is increased to reach 80% by 2009. ART, antiretroviral therapy; HIV+, human immunodeficiency virus–positive; IPT, isoniazid preventive therapy; PT, preventive therapy; TB, tuberculosis.