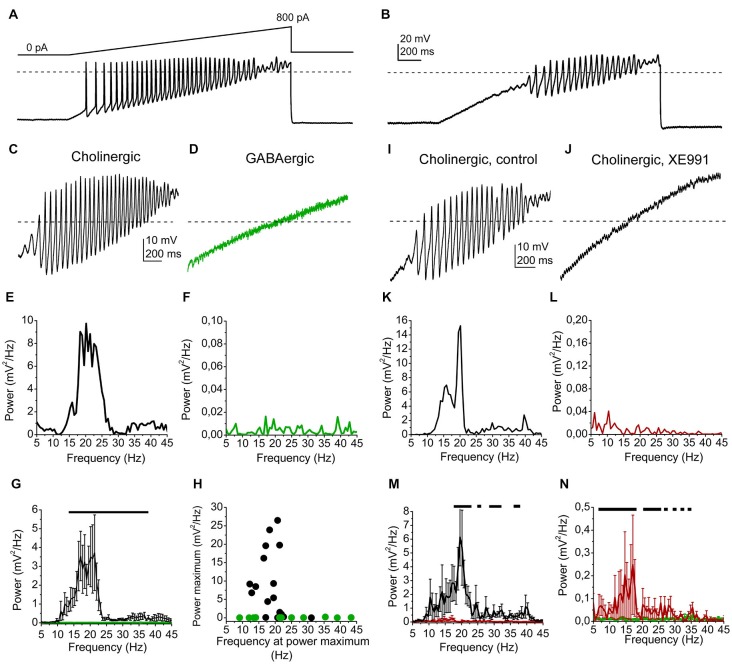
Figure 3.
High threshold membrane potential oscillations are affected by the M-current. (A) Representative voltage trace from a cholinergic cell elicited by a ramp of depolarizing current injection under control conditions. (B) Voltage trace from the same neuron in the presence of TTX. (C) High threshold oscillation recorded from a cholinergic neuron in the presence of TTX. (D) High threshold oscillation recorded from a GABAergic neuron in the presence of TTX. (E) Power spectrum of the oscillatory activity of the cholinergic neuron shown on panel (C). (F) Power spectrum of the oscillatory activity of the GABAergic neuron shown on panel (D). (G) Statistical summary of the power spectra of all recorded neurons (average ± SEM). Black: cholinergic, green: GABAergic. The black line indicates the frequency range where significant difference was found between datasets obtained from cholinergic and GABAergic neurons. (H) Power peaks plotted against the frequencies at the power maximum (black: cholinergic; green: GABAergic neurons). (I) High threshold oscillation recorded from another cholinergic neuron in the presence of TTX. (J) Records from the same neuron in the presence of 20 μM XE991. (K) Power spectrum of the oscillatory activity of the cholinergic neuron shown on panel (I). (L) Power spectrum of the oscillatory activity with XE991, shown on panel (J). (M) Statistical summary of the power spectra of all cholinergic neurons under control conditions (black) and with XE991 (red; average ± SEM). (N) Comparison of power spectra of cholinergic neurons in the presence of XE991 (red) and GABAergic neurons (green; average ± SEM). Black lines of panels (M,N) indicate the frequency ranges where statistical differences were found between the two examined populations of data. Dashed lines of panels (A–D) and (I,J) indicate 0 mV.