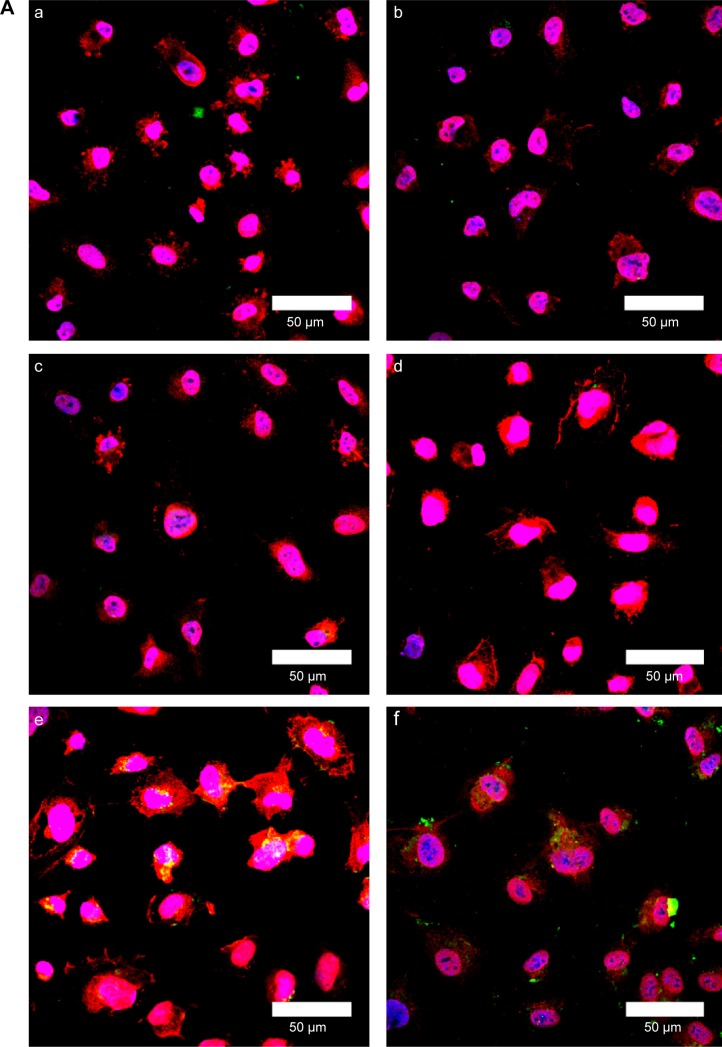
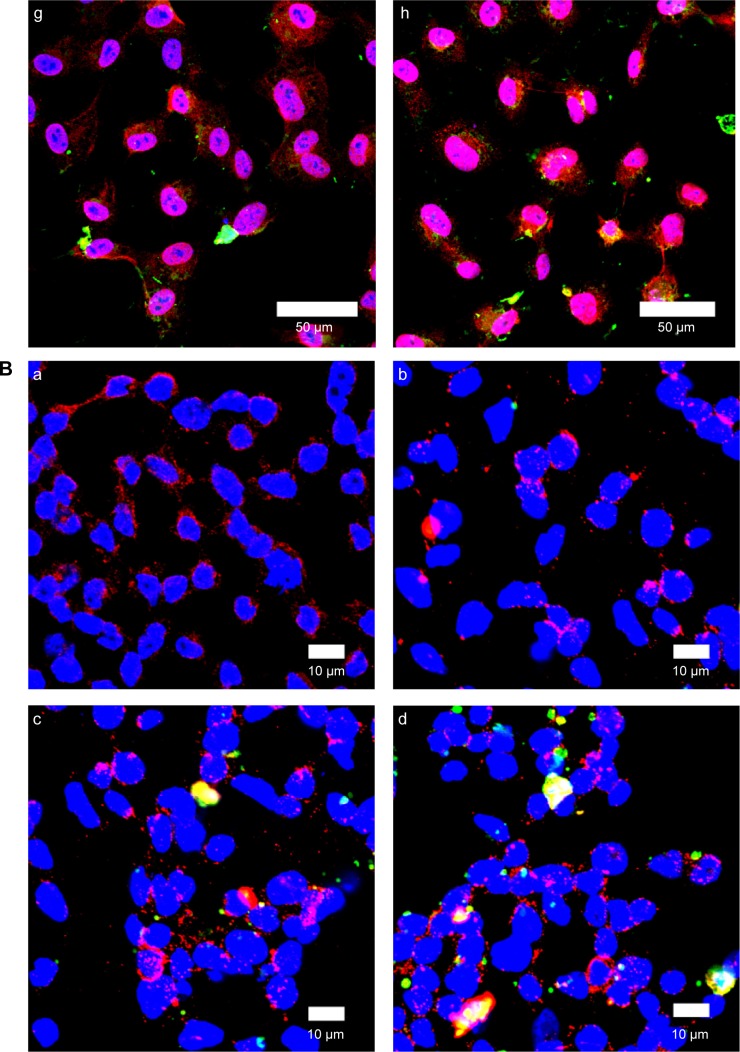
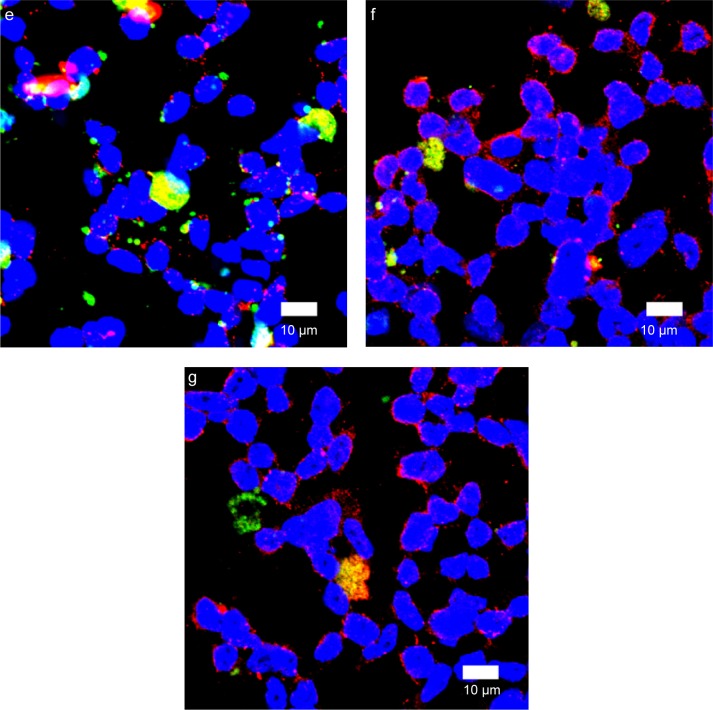
Figure 10.
(A) Immunochemical staining images of WGA-CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes interacting with HBMECs. (a–d) CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes; (e–h) WGA-CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes; (a) rCL =0%; (b) rCL =5%; (c) rCL =10%; (d) rCL =20%; (e) CWGA =2.5 mg/mL and rCL =10%; (f) CWGA =2.5 mg/mL and rCL =20%; (g) CWGA =5 mg/mL and rCL =10%; (h) CWGA =5 mg/mL and rCL =20%. Green WGA-CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes are adjacent to red O-linked N-acetylglucosamine near blue HBMEC nuclei. (B) Fluorescent images of WGA-CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes interacting with SK-N-MC cells with an insult of Aβ1–42. (a) Control; (b–e) CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes; (b) rCL =0%; (c) rCL =5%; (d) rCL =10%; (e) rCL =20%; (f) CWGA =5 mg/mL, rCL =10%; (g) CWGA =5 mg/mL, rCL =20%. The Aβ1–42 concentration is 10 μM. Green WGA-CL-NGF-CUR-liposomes attached on red Aβ1–42, which is deposited near blue SK-N-MC cell nuclei.
Abbreviations: CWGA, WGA concentration in grafting medium (mg/mL); rCL, CL mole percentage in lipids (%); CL, cardiolipin; CUR, curcumin; NGF, nerve growth factor; WGA, wheat germ agglutinin; HBMECs, human brain-microvascular endothelial cells; Aβ1–42, β-amyloid1–42.