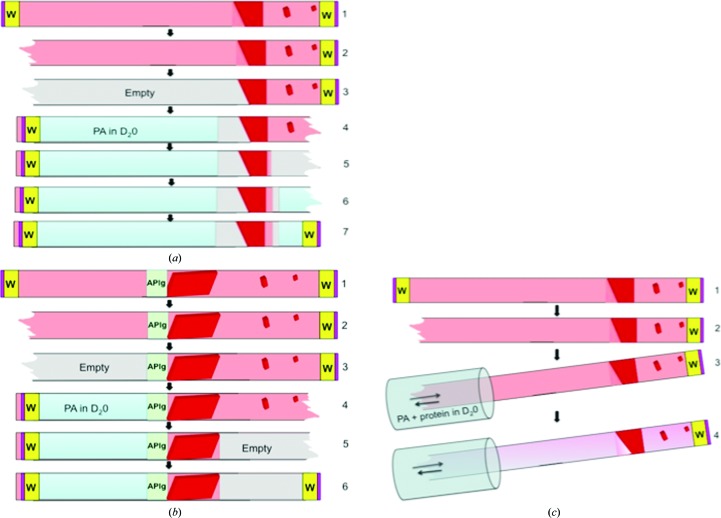
Figure 3.
Procedure for deuterium exchange in capillaries. Large-volume crystals grown or mounted in a large-diameter (>0.3 mm) quartz capillary can undergo D2O exchange quite readily. In the case where the crystals are grown in situ, the capillary ends can be excised and the solutions withdrawn one end at a time and replaced with precipitating agent (PA) in D2O (a). The exchanging D2O solution is placed close to the targeted crystal, leaving an air gap for vapor diffusion. When there is an agarose plug separating the precipitant and protein solutions, the precipitant is simply replaced with the D2O solution filled against the agarose plug while the other end is left empty (b). D2O exchanges can also directly diffuse into the existing precipitant solution with a solution containing deuterated precipitating agent and protein (c).