Figure 1.
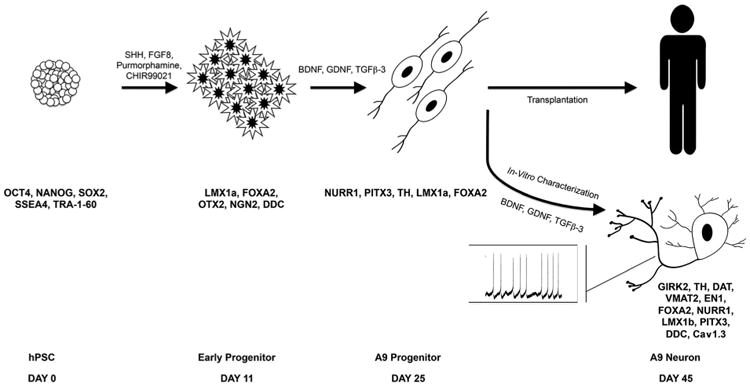
Schematic describing the floor plate–based method (Kirks et al., 2011) for generation of A9-type dopaminergic (DA) neural progenitors from hESCs. Here, hESCs and their progeny are exposed to key signaling molecules (SHH, WNT, and FGF8) in a temporally controlled manner to yield robust generation of A9-type DA neural precursors for transplantation. The cells co-express NURR1, LMX1a, and FOXA2 at approximately day 25, the stage at which they are used for transplantation. When allowed to differentiate in vitro, these cells develop clear A9 DA neuronal phenotypes by day 35–45, expressing key markers (GIRK2, Cav1.3, PITX 3, and TH) and exhibiting hallmark electrophysiological properties, including spontaneous bursting. For abbreviations, see list.
