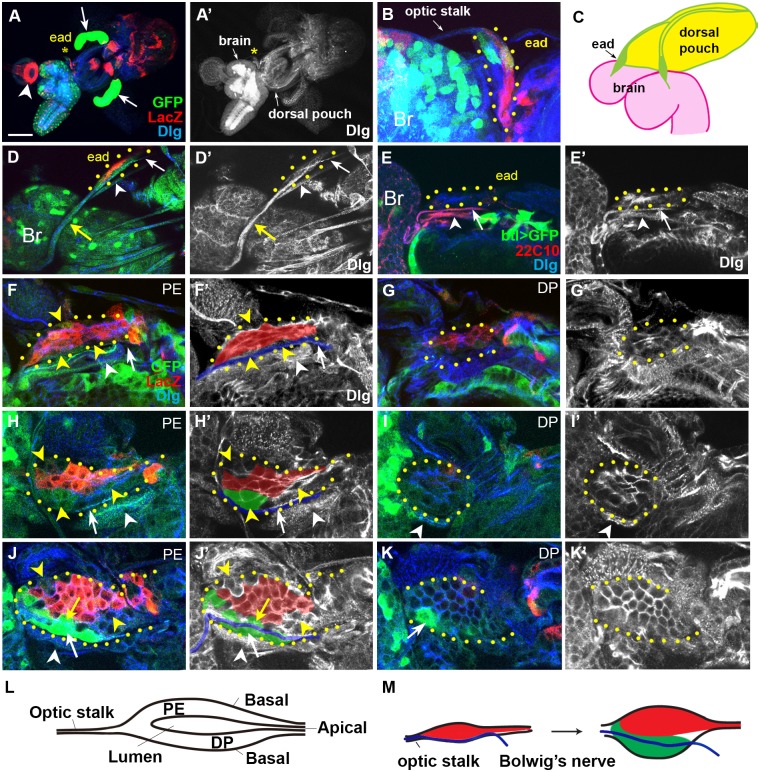
Fig 1. Growth of the ead from hatching to mid-L1 stage.
Cell boundary visualized with anti-Dlg antibody is marked with either blue (A-K), or white (A’-K’). wg-LacZ+ and dpp-Gal4+ cells are marked with red and green, respectively except (E). Confocal images of PE, DP, and both combined (COM) are indicated in upper right. Boundary of the ead is marked with yellow dots. (A, A’) Arrow and arrowhead in (A) indicate salivary gland and proventriculus, respectively. The eads are marked with asterisks. (B) Same sample shown in (A) is magnified to show the ead enclosed in a yellow-dotted circle. (C) A diagram of ead, brain, and dorsal pouch of the L1 ead. (D) Two nerve-like structures on the ventral side of the newly hatched early L1 ead. Arrow and arrowhead indicate Bolwig’s nerve and the unknown nerve, respectively. Yellow arrow points the optic stalk and the Bolwig’s nerve within. The sample is unusually stretched during preparation, making the two nerves easily distinguishable. (E) The Bolwig’s nerve (arrow) and the unknown nerve (arrowhead) are marked with a neuron-specific marker 22C10, not marked with GFP expression driven by a trachea-specific breathless-Gal4. (F, G) PE (F) and DP (G) layers of the ead from a newly hatched larva. Bolwig’s nerve is marked with white arrows (F, F’) and blue line (F’). (H, I) PE (H) and DP (I) layers of a little older ead. (J, K) A mid-L1 ead with cells expressing high level of dpp-Gal4 on the dorsal (yellow arrow in J) or ventral (white arrow in J) side of the Bolwig’s nerve (blue line in J’). (L) A cross-section of L1 ead is diagrammed. Apical surfaces of the PM and DP layers face each other in the disc lumen. (M) A diagram showing the formation of new ventral domain and the position of Bolwig’s nerve during this stage on the PE layer. Scale bar: A, 100 μm; B, D-E, 20μm; F-K, 10 μm.