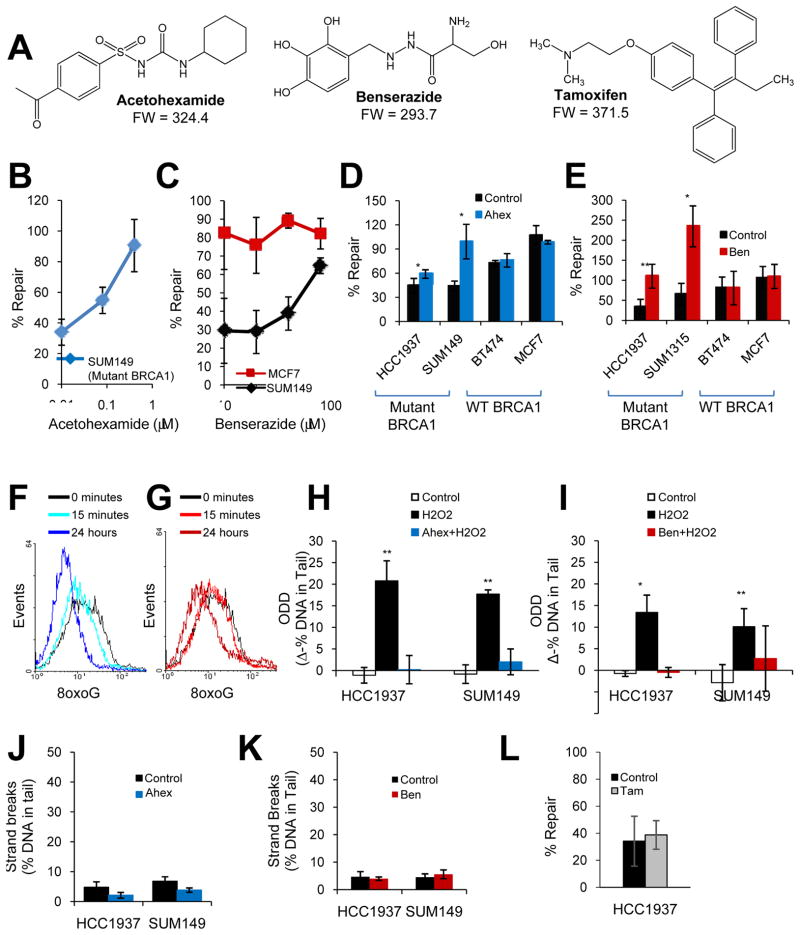
Fig. 2. DNA repair-activating agents enhance BER of ODD in the presence of mutant BRCA1.
(A) Chemical structures are shown for DNA repair-activating agents, acetohexamide and benserazide, and the FDA-approved chemoprevention agent for breast cancer, tamoxifen. (B–C) The graphs depict the effect of increasing concentrations of acetohexamide (B) or benserazide (C) on BER in SUM149 (mutant BRCA1) or MCF7 (wild-type BRCA1) cells. (D–E) The graphs illustrate the effect of vehicle control, 20μM acetohexamide (D), or 20μM benserazide (E) on BER in cell lines with mutant or wild-type BRCA1. (F–G) Basal levels of 8oxoG lesions in SUM149 cells treated with 20μM acetohexamide (F) or 20μM benserazide (G) for the specified time were determined by flow cytometry. A leftward shift in histogram peak indicates decreased 8oxoG levels. Data represent two independent experiments. (H–I) Levels of H2O2-induced ODD following pretreatment with vehicle control, 0.4μM acetohexamide (H) or 20μM benserazide (I) for 24 hours were compared to undamaged control for mutant BRCA1 cell lines using the alkaline comet assay modified for detection of oxidative lesions. Each bar represents the average of three experiments ± s.e.m. (J–K) DNA strand breaks in mutant BRCA1 cell lines treated with vehicle control, 0.4μM acetohexamide (J) or 20μM benserazide (K) for 28 hours were measured by the alkaline comet assay. (L) The bar graph indicates the effect of vehicle control or 1μM tamoxifen on BER in SUM149 cells. Unless otherwise indicated, all data are means and represent at least three independent experiments, error bars denote s.d., and p-values are relative to the control. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. Ahex, acetohexamide; Ben, benserazide; Tam, tamoxifen; 8oxoG, 8-oxoguanine adducts.