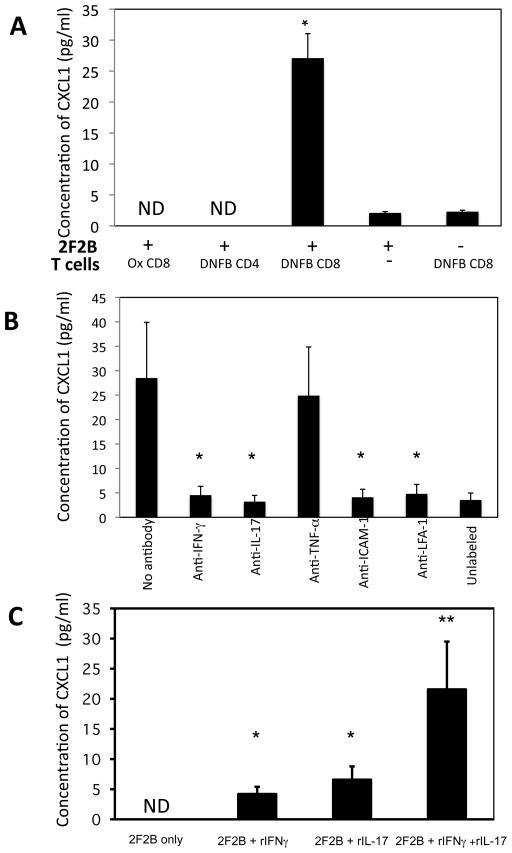
FIGURE 8.
Hapten-immune CD8 T cells induce endothelial cell production of CXCL1 in vitro. A. 2F2B endothelial cells were labeled with DNBS, washed 4 times, and 2 × 104 cells were cultured with 1 × 106 isolated CD4+ or CD8+ T cells from DNFB- or Ox-sensitized C3H mice. Culture supernatants were collected after 6 h and assessed for levels of CXCL1 by ELISA. The mean concentration ± SEM for 4 individual cell culture samples is shown. Results are representative of two individual experiments each. *p ≤ 0.05. B. DNBS-labeled or unlabeled 2F2B cells were cultured with purified CD8 T cells from the lymph nodes of DNFB-sensitized mice and 10 μg mAb to IFN-γ IL-17, TNF-α, ICAM, or LFA-1 was added to each culture as indicated. Culture supernatants were collected after 6 h and tested for CXCL1 by ELISA. The mean concentration ± SEM for 4 individual cell culture samples is shown. *p ≤ 0.05. C. Unlabeled 2F2B cells were cultured with 4 ng aliquots of rIFN-γ, rIL-17, or both recombinant cytokines. Culture supernatants were collected after 6 h and assessed for levels of CXCL1 by ELISA. The mean concentration ± SEM for 4 individual cell culture samples is shown. Results are representative of two individual experiments each. *p ≤ 0.05 vs. 2F2B only. **p ≤ 0.05 vs. cultures with individual cytokines added.