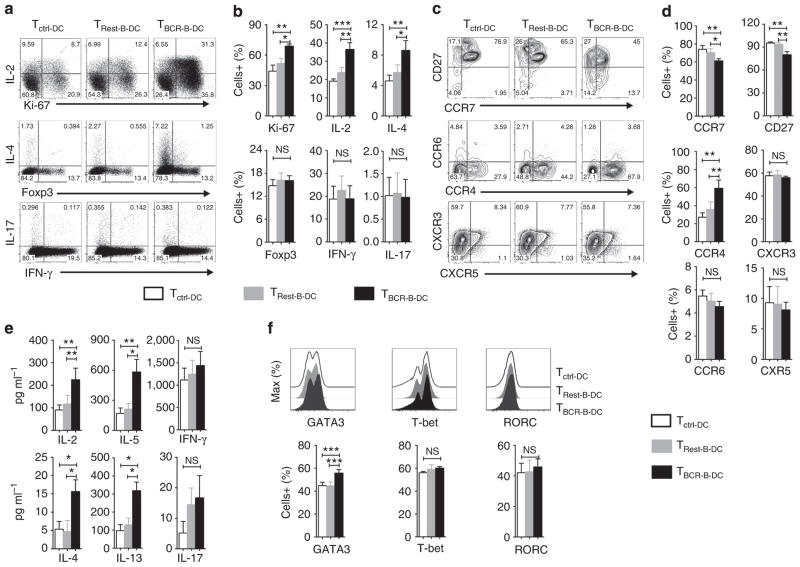
Figure 7. B cell-matured DCs favour polarization of naive CD4+ T cells to Th2 cells.
Immature DCs were cultured for 48 h in the medium containing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-4 alone (DCctrl), or co-cultured at 1:1 ratio with CD19 + B cells that were either in resting phase (DCRest-B) or directly activated in DC–B cell co-culture via BCR stimuli (DCBCR-B). DCs were purified from B cell–DC co-culture by depleting B cells. CD4 +CD45RO− naive Th cells were co-cultured with control DCs (Tctrl-DC) or activated B-cell-matured DCs (TBCR-B-DC) or resting B-cell-stimulated DC (TRest-B-DC) at the ratio of 20:1 for 6 days. (a,b) CD3 + T cells were analysed for the intracellular expression of cytokines and transcription factors by flow cytometry. Representative plot and mean±s.e.m. of data from ten donors. (c,d) CD3 + T cells were analysed for the surface phenotype by flow cytometry. Representative plot and mean±s.e.m. of data from five donors. (e) After 6 days, supernatants from DC–T cell co-cultures were analysed for various T-cell cytokines. Mean±s.e.m. of data from eight to ten donors. (f) CD3 + T cells were analysed for intracellular expression of transcription factors by flow cytometry. Representative plot and mean±s.e.m. of data from four donors. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; NS, not significant by one-way analysis of variance test.