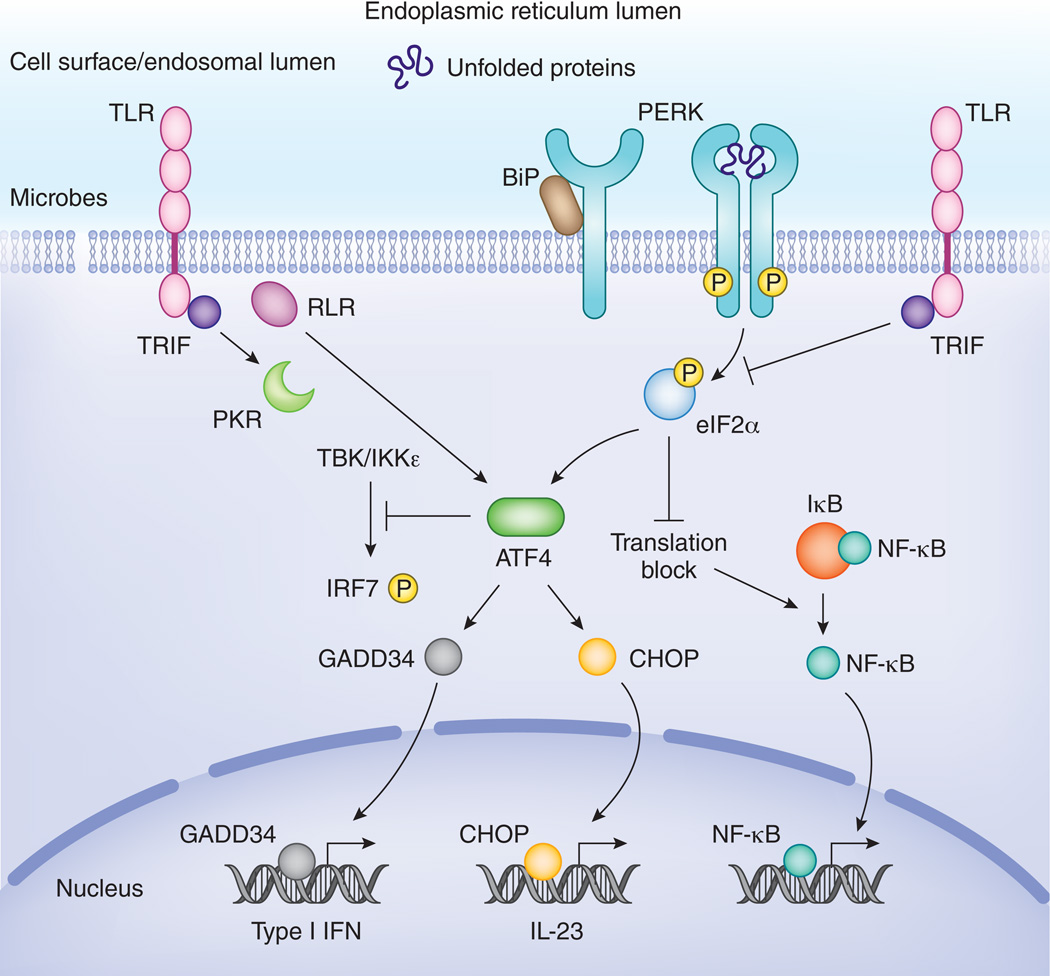
Figure 4. Pathways downstream of PERK are tightly controlled by inflammatory signals.
PERK-mediated translational inhibition leads to a shutdown of IκB de novo synthesis and as such leads to activation of NF-κB. ATF4 is involved in IFN and IL-23 cytokine expression via activation of GADD34 and CHOP respectively. On the other hand, it has also been reported that ATF4 interferes with TBK-IKKε mediated phosphorylation of IRF7 and IFN production in embryonic fibroblasts. TLRs tightly control the ATF4-CHOP branch and prevent induction of CHOP in macrophages, in a TRIF-dependent manner. In general, several microbial stress signals also lead to activation of ATF4, ATF3, CHOP or GADD34 in a PERK-independent, but TRIF, PKR or RLR-MAVS dependent manner. This microbial stress response hijacks components of the UPR, but has a different functional outcome.