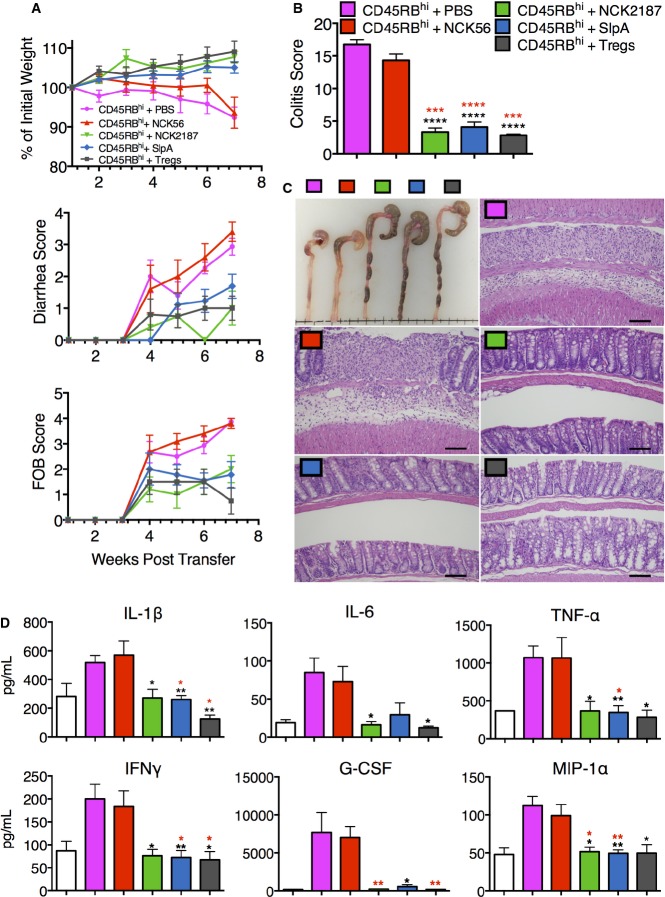
A B6
Rag1−/− mice were injected with 10
6 CD4
+CD45RB
hi T cells and then orally gavaged with NCK56 (red), NCK2187 (green), or SlpA (blue), 1 and 3 days after transfer, and subsequently once a week for four consecutive weeks, or left untreated (magenta). A group of mice was co-transferred with CD4
+CD25
+ T cells as a positive control for protection (Tregs; gray). Colitis severity was determined in part by weight loss, diarrhea scores, and FOB. See Supplementary
Tables S1, S2 and S3 for statistical analyses results.