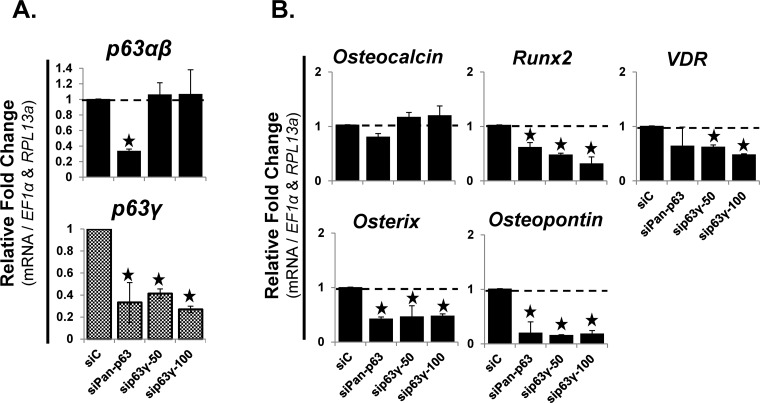
Fig 7. Targeted knockdown of p63γ variants decreased the mRNA expression of VDR, osterix, runx2 and osteopontin.
Knockdown of total p63 (siPan-p63; 50nM) or the p63γ (TAp63γ & ΔNp63γ) splice variants (sip63γ; 50nM or 100nM) in hMSC was done using transfection with siRNA (3 days). Osteogenic differentiation media was added on day-3 for 4 additional days; therefore, cells were collected 7 days post siRNA transfection. A) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA expression of p63 splice variants (top panel, p63α / β, bottom panel p63γ). RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA expression demonstrated the relative level of knockdown of the p63 splice variants by siPan-p63 & sip63γ compared to a scrambled control (siC). B) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers: VDR (vitamin D3 receptor (binds 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3)), Osteocalcin, Osterix, Osteopontin, Runx2 and BSP. No change was observed for BSP (data not shown). Alkaline phosphatase staining was also performed but no change was observed (data not shown). N = 3 independent experiments in duplicate. (*) p ≤ 0.05 compared to control (siC) which were set to the value of “1”. hMSC used were from a 22 year old male.