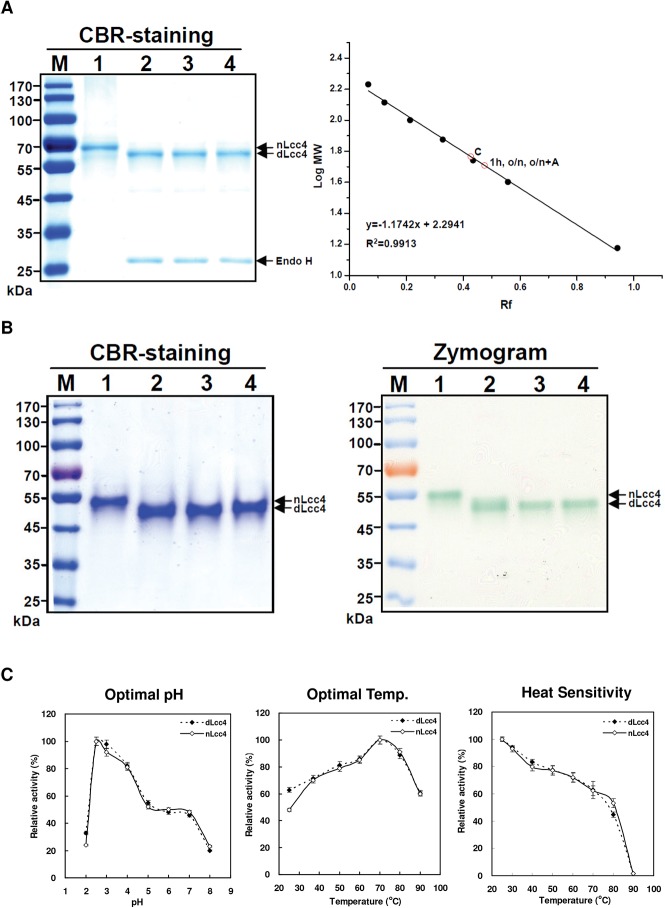
Fig 2. Analysis of molecular weight and enzymatic activity of native and Endo H-deglycosylated Lcc4 by 10% SDS-PAGE and zymography.
(A) Heated laccases were separated and visualized by coomassie brilliant blue (CBR) staining and their relative mobility distances (Rf values) and molecular weights were calculated and calibrated with a set of molecular weight standards. (B) Unheated laccase samples in lysis buffer, in which the enzymes were not denatured and remained active, were separated and visualized by CBR staining and zymographic analysis using ABTS substrate. Protein marker (M), native Lcc4 (nLcc4, lane 1), nLcc4 treated with Endo H for 1 h (lane 2), overnight (lane 3), and with an extra supplement of 500 U Endo H in the overnight treatment (lane 4). (C) Optimal pH, optimal temperature and temperature sensitivity determination of nLcc4 and Endo H-deglycosylated Lcc4 (dLcc4). In the temperature sensitivity assay, laccase enzyme was pre-incubated at the indicated temperature for 10 min, and the residual enzymatic activity was then immediately measured. Black rhombi: nLcc4; white rhombi: dLcc4.