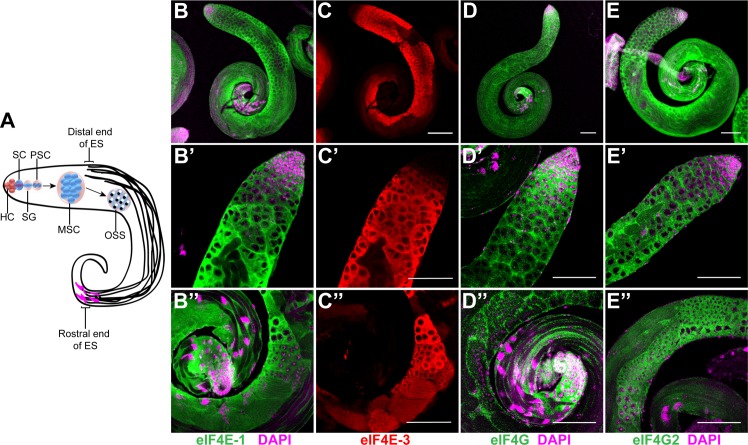
Fig 1. Distribution of eIF4E-1, eIF4E-3, eIF4G and eIF4G2 in the wild-type testes.
(A) Schematic diagram showing the stages of spermatogenesis in Drosophila testes. The hub cells (HC) at the apical tip of the testes maintain the stem cells (SC) which include a germline stem cell and a somatic cyst stem cell. The germline stem cell differentiates into spermatogonia (SG) which divide mitotically to produce primary spermatocytes (PSC). The spermatocytes undergo rapid cellular growth to form mature spermatocytes (MSC) that undergo meiosis, producing haploid onion stage spermatids (OSS). Following cellular transformation and differentiation, they develop flagella with the nuclei (magenta) at the distal end of the testes. ES = Elongated spermatids. Whole-mount immunostaining of adult testes using antibodies that recognise eIF4E-1 (B-B'', green), eIF4E-3 (C-C'', red), eIF4G (D-D'', green) and eIF4G2 (E-E'', green). The top panel (B-E) shows the entire testes while the middle (B'-E') and lower panels (B''-E'') show the apical and distal end, respectively. DAPI is shown in magenta. Scale bar 100 μm.