Fig. 2.
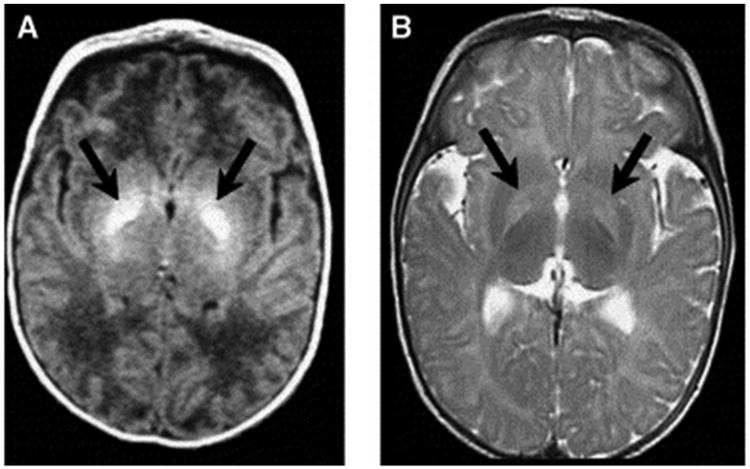
Axial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of bilateral hyperintense lesions in the globus pallidus in axial projections (arrows). (A) T1-weighted axial image of a six-day-old, 37-week gestation boy with peak total bilirubin of 34.6 mg/dL. At age seven years, this child was highly intelligent, but moderately to severely disabled with dystonic, athetoid kernicteric cerebral palsy; he ambulates with a walker. (B) Axial T2-weighted MRI of a two-year-old who has classic dystonic kernicterus. Note the increased intensity of the globus pallidus bilaterally (shown with arrows and dotted line on right side only). There were no abnormalities noted in brainstem or cerebellum. (Panel (A) reprinted with permission from Shapiro SM, Bilirubin toxicity in the developing nervous system. Pediatric Neurology 2003;29:414. Panel (B) and Fig. 2 caption reprinted from Shapiro et al. [28].)
