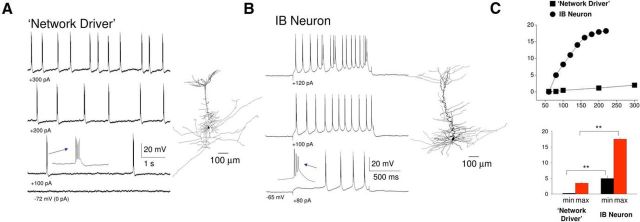
Figure 8.
“Network driver” cells possess distinct intrinsic properties compared with conventional IB neurons. A, In the absence of CCH, steady depolarizing current injection elicits rhythmic low-frequency bursting in a “network driver” IB neuron. Inset, A single burst. The reconstructed neuron is illustrated on the immediate right. B, In the absence of CCH, depolarizing current steps elicit rhythmic bursts in a conventional IB neuron at notably higher frequencies than observed for the “network driver” neuron depicted in A. The reconstructed neuron is illustrated on the immediate right. C, Top, Plot showing frequency of rhythmic bursting versus injected current for the “network driver” neuron shown in A (squares) and the conventional IB neuron shown in B (circles). Bottom, Average minimum and maximum frequencies of rhythmic bursting for 6 “network driver” neurons and 8 conventional IB cells.