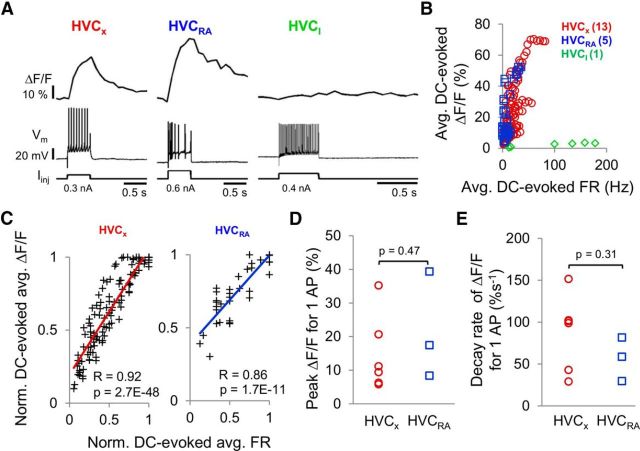
Figure 2.
Calcium signals in HVC PNs are correlated with action potential activity in brain slice preparations. A, Examples of simultaneously recorded calcium signals (ΔF/F) and action potentials evoked by positive, intrasomatic current injection into an HVCX cell (left), HVCRA cell (middle), and HVCI cell (right). B, Average DC-evoked ΔF/F plotted against average DC-evoked firing rates for all three cell types (HVCX: n = 13 cells, red circles; HVCRA: n = 5 cells, blue squares; HVCI: n = 1 cell, green diamonds). C, Normalized average DC-evoked ΔF/F was significantly correlated with normalized average FR in HVCX cells (left, r = 0.92, p = 2.7E-48, linear regression) and in HVCRA cells (right, r = 0.86, p = 1.7E-11). Calcium responses and firing rates were each normalized to their respective maximum values obtained within each cell. Lines indicate linear fits. D, E, Mean peak responses and decay rates of the peak calcium signals associated with DC-evoked single action potentials were not significantly different between the two PN types (peak ΔF/F-HVCX: 14.6 ± 4.6%, HVCRA: 21.7 ± 9.2%; decay rates HVCX: 87.6 ± 18.3%s−1, HVCRA: 56.7 ± 15.0%s−1; mean ± SEM, two-tailed t test, both p > 0.05).