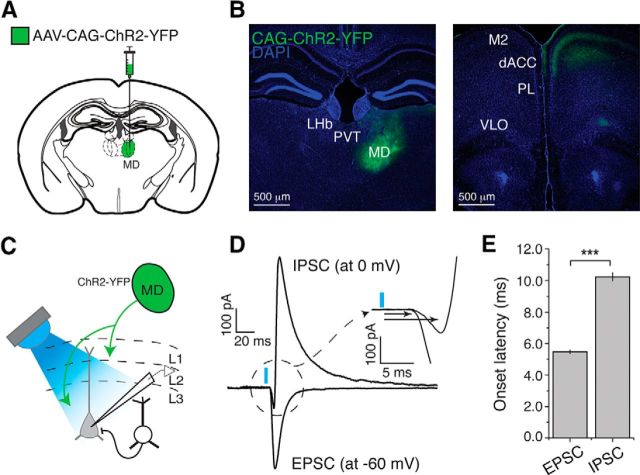
Figure 1.
Inputs from MD drive excitation and inhibition onto layer 3 dACC pyramidal neurons. A, Schematic of injection into the MD. B, Left, Representative image of a brain section in which the MD was injected with AAV-CAG-ChR2(H134R)-YFP. Right, Image of a brain section from the same mouse showing the dACC area where ChR2-YFP-expressing axons originating from the MD are clearly visible in layers 1, 3, and 5. LHb, Lateral habenula; PVT, paraventricular thalamus; M2, secondary motor cortex; PL, prelimbic cortex; VLO, ventral and lateral orbital cortex. C, Layer 3 pyramidal neurons in dACC were recorded while MD axons were photo-stimulated. D, IPSCs and EPSCs were recorded at 0 mV and −60 mV, respectively, holding potentials. MD axon stimulation elicited a short-latency monosynaptic EPSC followed by a delayed IPSC. Inset, Enlarged view of the circled area, in which the two arrows indicate the onset of EPSC and IPSC. E, Onset latency of light-evoked IPSCs was longer than that of light-evoked EPSCs. ***p < 0.0001. Data are mean ± SEM.