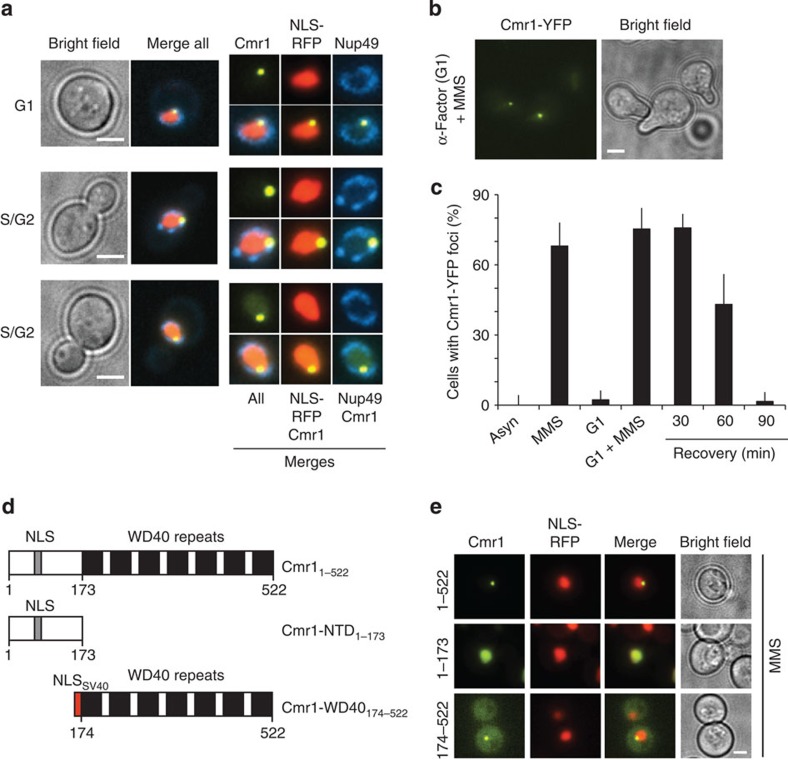
Figure 2. Cmr1 localizes into perinuclear foci.
(a) Cmr1 foci localize at the nuclear periphery. Cells expressing Cmr1-YFP (IG66) were transformed with pNEB21 for expression of Nup49-CFP and pML84 for expression of NLS-yEmRFP, and treated with 0.05% MMS. Cmr1 localization relative to the nucleoplasm and the nuclear membrane is shown in both unbudded (G1) and budded (S/G2) cells. Nuclear zooms are at 150%. (b) Cmr1 foci in α-factor-arrested cells. Cells (IG66) were cultured with α-factor for 1 h, followed by treatment with 0.05% MMS for 2 h. (c) Quantification of Cmr1 foci. The percentage of cells (IG66) with Cmr1-YFP foci was quantified in asynchronous and G1-arrested populations, before and after treatment with 0.05% MMS for 1 h, and 30, 60 and 90 min after the drug was removed. Two to 3 replicates of 100–200 cells were analysed for each condition. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. (d) Schematic representation of Cmr1 and truncation constructs. (e) The WD40 domain of Cmr1 is necessary and sufficient for relocalization into foci. Cmr1-YFP constructs containing the full-length protein (pIG13), the N-terminal (pIG14) or WD40-containing portion of the protein (pIG15) were expressed from a 2-μm plasmid in cells (ML657) harbouring NLS-yEmRFP, and relocalization of Cmr1 into nuclear foci was monitored after treatment with 0.05% MMS. Scale bars, 2 μm.