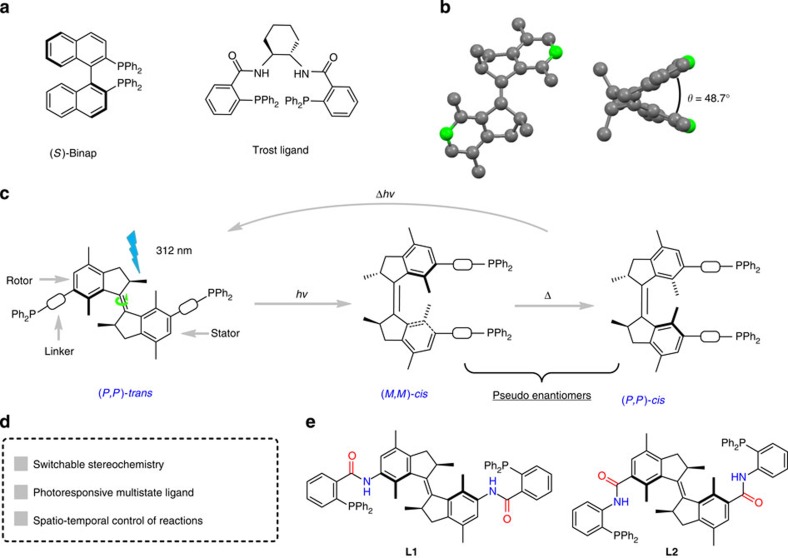
Figure 1. Chiral photoresponsive phosphine ligands.
(a) Traditional C2-symmetric privileged ligands: (S)-Binap and Trost ligand. (b) Crystal structure of the parent molecular motor25; left: (S,S)-(M,M)-trans isomer, right: (R,R)-(P,P)-cis isomer. (c) Novel three-state photoresponsive phosphine ligand based on unidirectional molecular motor. The (P,P)-trans ligand based system might actually represent several catalytic complexes in the multi-state system, that is, oligomeric/polymeric P-Pd-ligand-Pd-ligand-Pd species due to phosphine ligand coordination in a monodentate manner to the metal. (d) Key features of novel chiral photoresponsive phosphine ligands. (e) Two potential photoresponsive phosphine ligands L1 and L2 incorporating amide linkers. R and S are used to define the chirality of the stereogenic centres; P (plus) and M (minus) are used to define the helicity of right and left-handed helix, respectively.