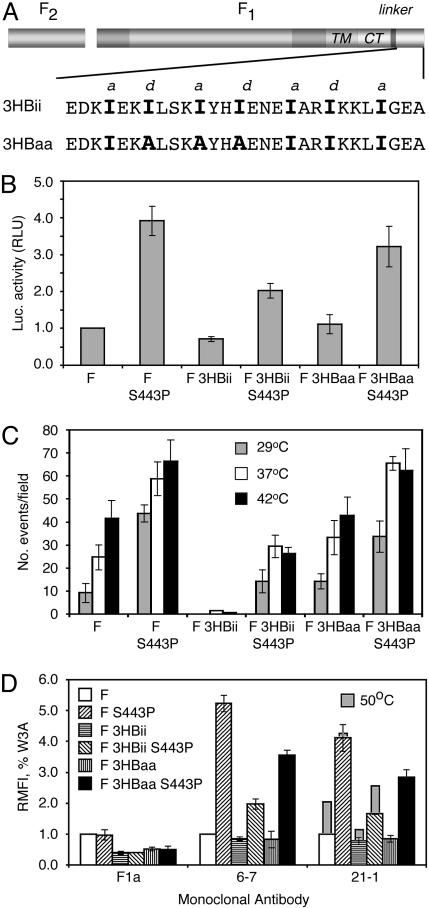
Fig. 3.
A cytoplasmic three-helix bundle (3HBii) domain stabilizes the SV5 F protein trimer. (A) Schematic diagram of WT W3A F containing a CT with a flexible linker (SGGSGG) and the 3HBii domain. The amino acid sequence of 3HBii [derived from GCN4-p-II (26)] and a mutant 3HBaa designed to ablate the isoleucine knob-into-hole helical interactions of 3HBii, and thus prevent 3HB formation, is shown. (B) Cell–cell fusion of WT F, F-3HBii, and F-3HBaa (with and without the S443P mutation) was measured by using the luciferase reporter gene activity assay. (C) Quantification of the average number of fusion events from 7–10 microscope fields for each F protein was determined by using the R18/6-carboxyfluorescein dye transfer assay. (D) mAb reactivity (RMFI) of transfected cells having very similar levels of F protein surface expression (as determined by biotinylation) of WT and mutant F proteins as measured by flow cytometry.