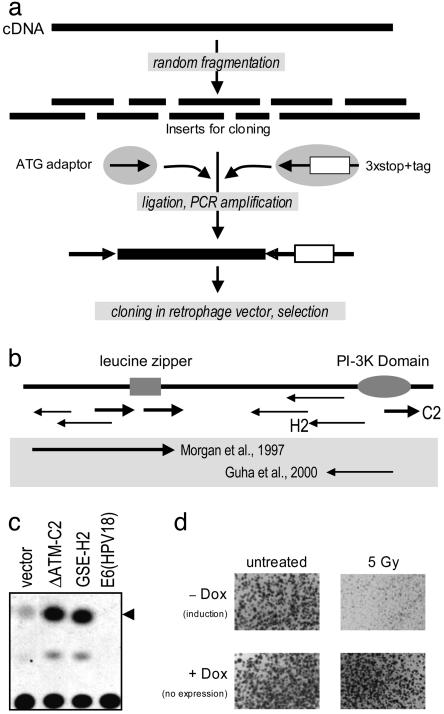
Fig. 3.
Isolation of genetic suppressor elements against ATM. (a) The ATM cDNA was randomly fragmented by using DNaseI, and the subsequent fragments were ligated to two adaptors. One adaptor contains the start codon whereas the other contains stop codons in all three reading frames and the tag, an 80-bp random sequence. The tagged GSEs were PCR amplified by using primers specific for each adaptor and cloned into the retrophage vector. Selection was performed in U2-OS cells. (b) Several GSEs were isolated, including both antisense and dominant negative peptides in comparison with the full-length protein and previously published inhibitors (20, 21) (shown in the gray zone). The coordinates of isolated GSEs and the nature of their products are listed in Table 1. (c) Individual GSEs were transiently transfected with a p53-responsive CAT reporter to measure p53 transcriptional activity. Higher activity was observed in the presence of both antisense and sense GSEs in accordance with previously published results (20–23). (d) The radiosensitizing activity of ΔATMC2 was further confirmed by recloning into a tetracycline-regulated retroviral vector and infected in U2-OS. In the absence of doxycycline, the GSE is expressed and had no effect on cell growth under normal conditions of cultivation [compare colony sizes in +Dox (induction) and -Dox (no expression) plates]. However, activation of the GSE expression significantly sensitizes U2-OS to 5 Gy of γ radiation.