Figure 5. Proposed Recombination Pathways.
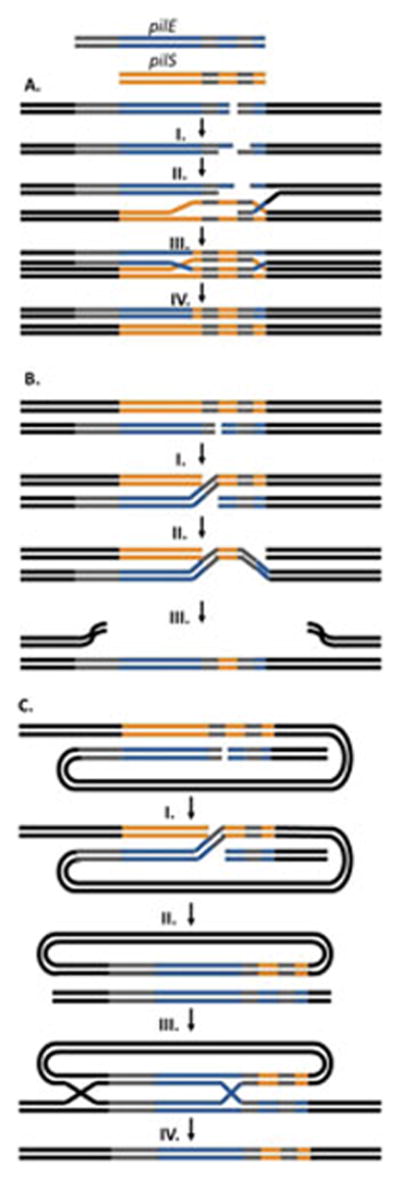
A. Unequal Crossing Over Model – A dsDNA break occurs at the pilE locus and I. the 5′ ends are resected by RecBCD to leave 3′ overhangs. II. A single 3′ end mediated by RecA, invades the pilS locus forming a D-loop. III. The 3′ ends are extended by DNA polymerase using the pilS gene as a template. IV. Resolution of the double Holliday junctions results in a new pilE sequence without altering the donor pilS sequence.
B. Successive Half Crossing Over Model – Recombination begins with a dsDNA break or single-stranded gap in pilE in a region of homology. I. A RecA and RecOR mediated half crossing over event occurs linking the pilE and a pilS locus on a sister chromosome. II. A second half crossing over event occurs in another region of microhomology downstream of the first event between the pilE:pilS hyrbid and the original pilE locus. III. This recombination event leads to a new sequence at the pilE locus and destruction of the donor chromosome.
C. Hybrid Intermediate Model – Similar to the half crossing over model, recombination initiates with a double stranded break or single-stranded gap at pilE and I. a half crossing over event with a donor pilS on the same chromosome. II. This results in a pilE:pilS hybrid intermediate and the loss of the donor chromosome. III. The hybrid intermediate then undergoes two recombination events with the recipient pilE on a different chromosome. The first recombination event would occur in the extensive region of homology upstream of the genes while the second even would utilize microhomology within the variable regions of the genes. IV. Resolution of the Holliday junction intermediates leads to a new pilE sequence on the recipient chromosome.
