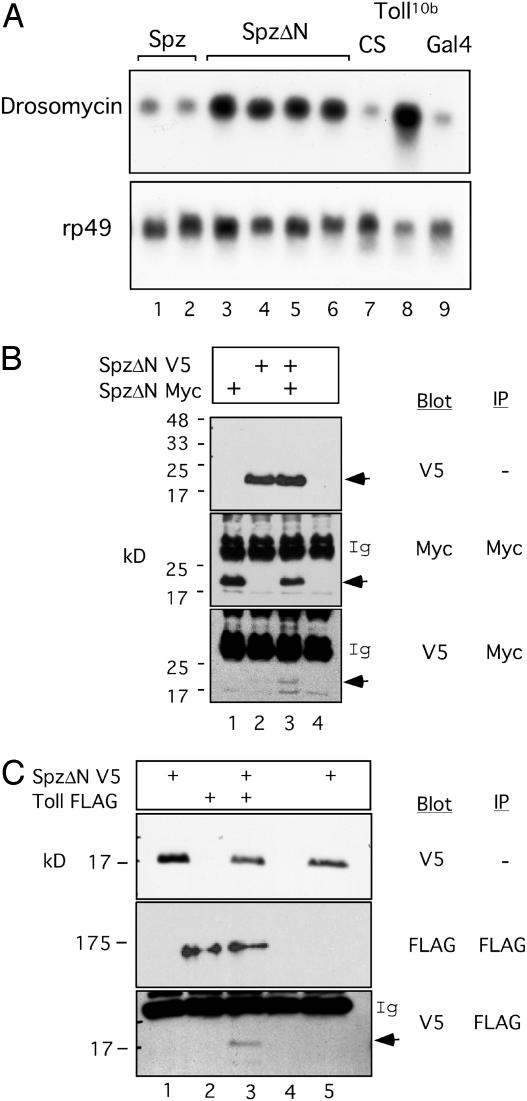
Fig. 1.
SpätzleΔN multimerization and interaction with Toll. (A) Northern blots of female transgenic lines containing YP1-Gal4 and UAS-SpätzleV5 (Spz) or UAS-SpätzleΔNV5 (SpzΔN). drosomycin or ribosomal protein 49 (rp49) probes were used for hybridization. Two independent Spz (lanes 1 and 2) and four independent SpzΔN transgenic lines (lanes 3–6) were assayed. The Can-tonS (CS) wild-type flies, Toll10b mutant flies, and YP1-Gal4 (Gal4) flies were included for comparison. It can be seen that SpzΔN can activate drosomycin expression efficiently. (B) Co-IP assays of fly lines containing SpätzleΔNV5, SpätzleΔNMyc, or both. The control line used was Gal4 (lane 4 in each panel). Antibodies used for Western blot or IP are as indicated. The proteins were separated on an SDS/15% PAGE gel. Ig indicates the immunoglobulin bands, and the arrows indicate SpätzleΔN, which runs as an ≈20-kDa protein. The blot shows that the two tagged proteins form a complex in the extract (bottom panel). (C) Co-IP assay of transgenic lines containing the indicated constructs crossed with YP1-Gal4. Lanes 1 and 5 were from two independent crosses of SpätzleΔNV5 with YP1-Gal4. Lane 4 was from Gal4 control flies. Antibodies used for Western blot or IP are as indicated. Toll-FLAG runs as a 175-kDa protein. Co-IP was detected only when both proteins were present in the same fly extract (bottom panel, lane 3).