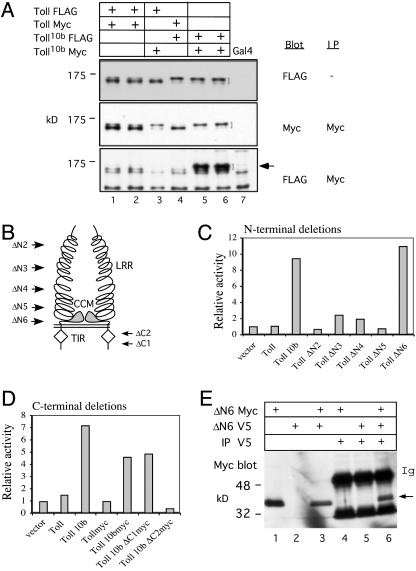
Fig. 2.
Multimerization of constitutively active Toll mutants. (A) Co-IP assays of recombinant fly lines containing various combinations of epitope-tagged Toll and Toll10b constructs. Two independent lines of Toll-FLAG/TollMyc (lanes 1 and 2), one line each of Toll-FLAG/Toll10bMyc and TollMyc/Toll10bFLAG (lanes 3 and 4), and two independent lines of Toll10bFLAG/Toll10bMyc (lanes 5 and 6) were used for the assay. Toll10b is more highly glycosylated than wild-type Toll and runs as a bigger protein (indicated by the brackets) (27, 29). The bottom panel shows that when both copies of tagged Toll10b are present, significant co-IP can be observed (indicated by the arrow). We did not observe any substantial complex formation for wild-type Toll, even after repeated trials. (B) Schematic representation of a Toll dimer. The extracellular LRR, the cysteine-containing motif (CCM), and the intracellular TIR domain are as labeled. The N-terminal deletion constructs all contain the first 34 aa fused with different lengths of C termini by a XbaI linker. The arrows indicate the approximate fusion points of the deletions (see Materials and Methods). ΔN1 is the same as the full-length protein except it contains a linker after aa 34, and, therefore, it is not included here. (C) Gene regulation by the N-terminal deletion constructs. N-terminal deletion constructs were expressed under the control of the Actin5C promoter, and their gene regulatory activities were assayed by cotransfection in S2 cells. The drosomycin-luciferase reporter was cotransfected, and the relative luciferase activity based on the Actin5C vector control is shown. All transfection results represent the average of three independent experiments. (D) Cotransfection assay of the C-terminal deletion constructs. These two deletion constructs also contain the Toll10b point mutation. The constructs were generated in the pUAST vector, and Actin5C-Gal4 and drosomycin-luciferase plasmids were included in the cotransfection. These two constructs contain the Myc tag, and, therefore, the Myc-tagged Toll and Toll10b constructs were included for comparison. (E) Co-IP assay of V5- and Myc-tagged ΔN6 in transfected S2 cell extracts. The cell extracts (lanes 1–3) and immunoprecipitates of V5 antibodies (lane 4–6) were analyzed by SDS/PAGE. Anti-Myc antibody was used for the Western blot. The blot shows that the region containing the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains is sufficient for multimerization.