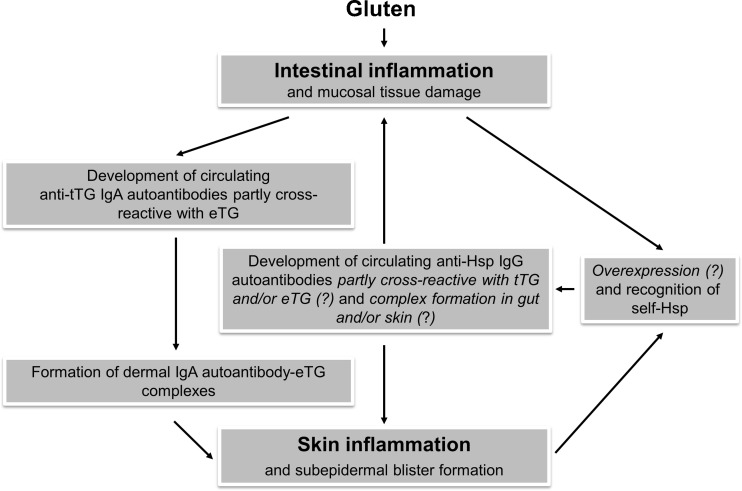
Fig. 3.
Putative pathophysiologic role of IgG autoantibodies to Hsp 60, 70, and 90 in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. Anti-Hsp autoantibodies partly cross-reactive with tTG and/or eTG may originate from inflamed intestinal tissue in the context of underlying celiac disease, the pathologic skin condition itself or both. Resulting immune complexes formed in the skin and/or gut may amplify and perpetuate inflammatory processes (e.g., by augmented proinflammatory cytokine production and costimulatory MHC-II expression via enhanced Hsp (receptor) cross-linking-mediated intracellular signaling events and/or by mimicking pathogenic activity of anti-tTG/eTG autoantibodies in terms of cross-reactivity) known to occur in dermatitis herpetiformis patients