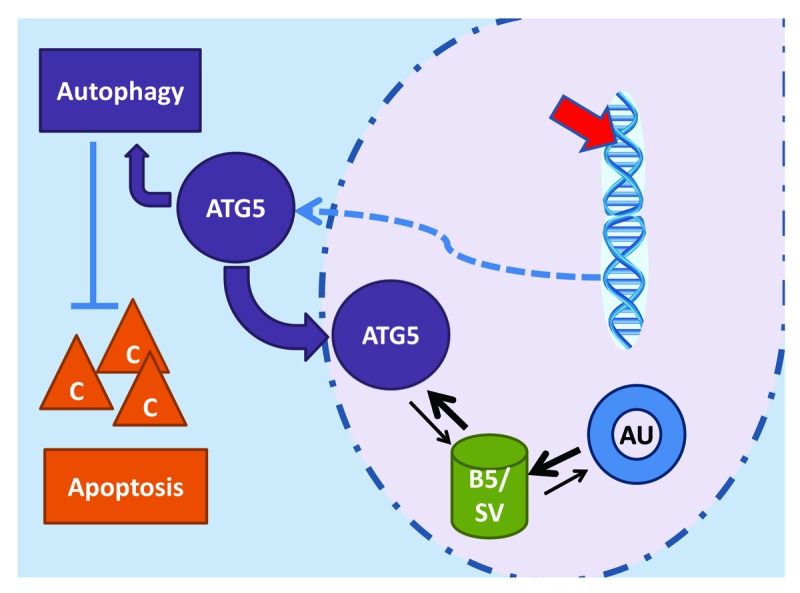
Figure 1. Low levels of DNA damage can be achieved with sublethal etoposide or cisplatin treatment, activating both apoptotic and autophagic pathways. The strongly upregulated ATG5 expression initiates autophagy, preventing caspase (C) activation and apoptosis. Much of the ATG5 is translocated to the nucleus, where it preferentially binds BIRC5/survivin (B5/SV), sharply reducing the availability for AURKB (AU) association, as needed for correct functioning of the chromosome passenger complex.
