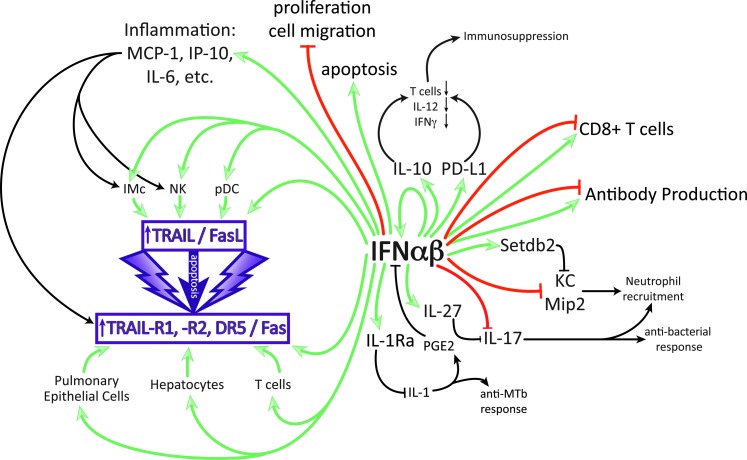
FIG. 1.
Multiple effects of IFN-αβ on immune and epithelial cells that can contribute to disease in specific infections. Only direct enhancing (green) and inhibitory (red) effects by IFN-αβ are color coded, secondary effects are in black. IFN-αβ can enhance production of IL-10, proinflammatory cytokines, and IL-27 and can block directly or indirectly the cytokines, IL-1, IL-12, IL-17, IFN-γ, and KC. Detrimental effects can be due to the suppression of antibacterial responses (IL-1, IL-17, IFN-γ, and KC) or to overstimulation of inflammation leading to damage by apoptosis of tissue cells or immune suppression by apoptosis of immune cells.