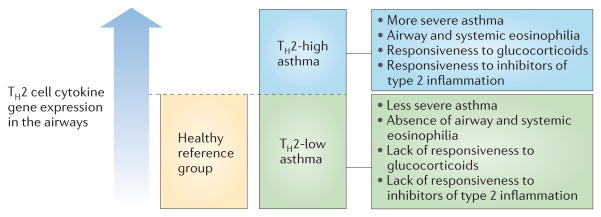
Figure 3. Asthma can be divided into TH2-low and TH2-high subgroups.
Levels of gene expression for T helper 2 (TH2) cell cytokines76 or for the activation of epithelial cells by TH2 cell cytokines77 show a continuum in the airways of patients with asthma (rather than a bimodal distribution). Individuals with asthma who have expression levels higher than the range found in healthy controls have specific clinical, pathological and treatment-response characteristics. This suggests a threshold effect of TH2 cell cytokines in the airways above which type 2 inflammation influences the clinical features of asthma and the responsiveness to specific treatments. Biomarkers of type 2 inflammation in blood and exhaled air can identify individuals with asthma who are above and below this threshold, and are showing promise as predictors of responsiveness to a growing list of type 2 cytokine inhibitors that are in late-phase clinical trials for asthma.