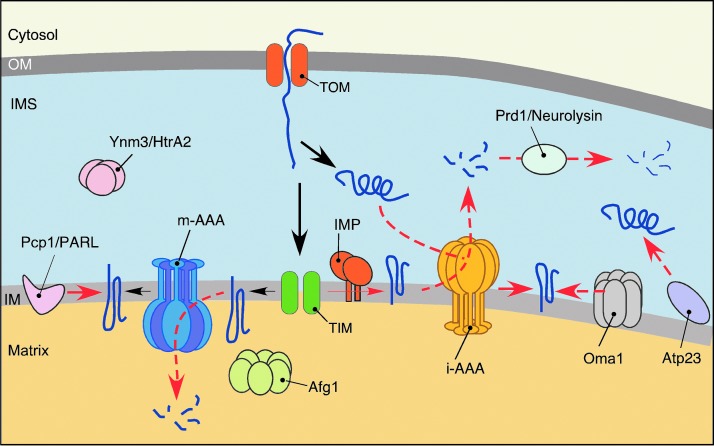
FIG. 5.
PMQC in the IM and intermembrane space (IMS). Complexity of mitochondrial IM anticipates vastly efficient systems to maintain protein homeostasis. These include two tightly coordinated proteases matrix-facing AAA metalloprotease (m-AAA) and intermembrane space-facing AAA metalloprotease (i-AAA), which along with other regulatory functions recognize excessive, misassembled, and damaged subunits of OXPHOS complexes associated with the IM. Another IM protease complex Oma1, with m-AAA-overlapping functions, is also proposed to play a major role in mitochondrial dynamics and homeostasis upon stress conditions. Rhomboid-like Pcp1/PARL protease is implicated in the intramembrane proteolysis of several IM proteins in yeast, whereas in mammalian cells, it also contributes to regulation of mitochondrial turnover. The IMS PMQC is less studied. In addition to the i-AAA, which exerts both proteolytic and chaperone functions toward IMS-localized proteins, the IMS subproteome appears to be regulated by oligopeptidase Prd1/Neurolysin and serine protease Ymn3/HtrA2. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars