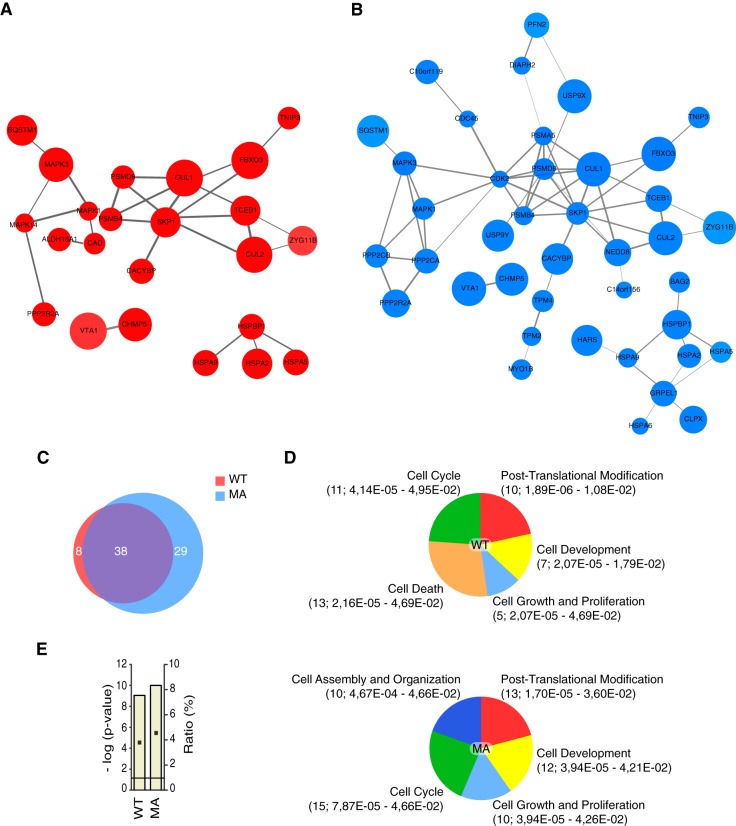
Fig. 1.
Emergent properties of the interactome of wild-type and constitutively active mDia2. A, Interaction map of wild-type mDia2. Proteins interaction maps were obtained as described in the Experimental Procedures. The maps contain only those mDia2-binding proteins reported to entertain interactions in the STRING database according to the specified criteria. B, Interaction map of constitutively active mDia2. Proteins interaction maps were obtained as in A. C, The overlap between the interactome of wild-type and constitutively active mDia2 is 50.7%. Venn diagram showing the number proteins unique to either wild-type (WT; red) or constitutively active (MA; blue) mDia2, as well the number of the common ones (purple). Percentage of overlap was obtained as follows: common proteins (38)/total nonredundant proteins (75) × 100. D, mDia2-binding proteins cluster into common and conformation-specific functional groups. Proteins binding to wild-type (WT) and constitutively active (MA) mDia2 were assigned to pathways regulating biological processes that define a functional group in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). Between brackets are: number of proteins specific for the indicated functional group; range of Fischer's Exact t test p values of the biological processes associated with the indicated functional group (supplemental Table S1, Sheet 4). E, mDia2 is linked to the protein ubiquitination pathway. The IPA protein ubiquitination pathway is the top canonical pathway in the interactome of both wild-type (WT) and constitutively active (MA) mDia2. Bar graphs show Fischer's Exact t test p values (as -log (p-value)), and ratios (% of the clustered proteins with respect to the total number of proteins belonging to the IPA protein ubiquitination pathway).