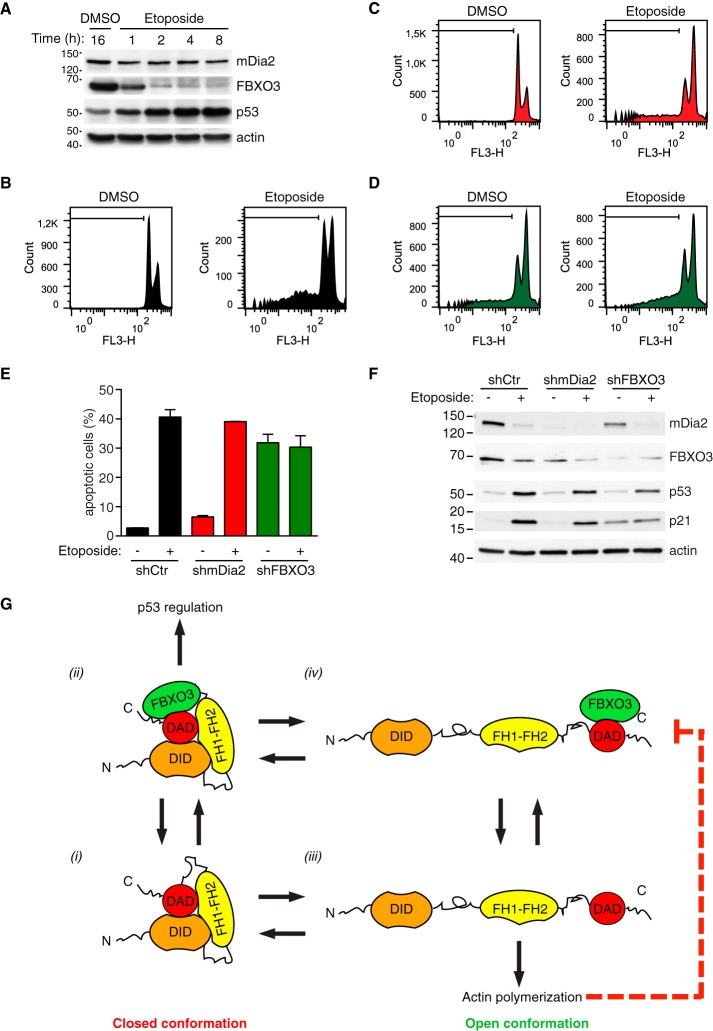
Fig. 7.
FBXO3 knockdown attenuates p53-mediated apoptosis upon DNA damage. A, Up-regulation of p53 is an early effect of etoposide. U2OS cells were treated with etoposide (20 μm) or DMSO and total cell lysates prepared at the indicated time (h = hour) and immunoblotted as indicated. One of two similar experiments is shown. B–D, DNA content in control, mDia2 knockdown and FBXO3-knockdown cells is affected by etoposide treatment. U2OS cells were infected with control (shCtr), mDia2-targeting (shmDia2) and FBXO3-targeting (shFBXO3) viruses. Cells were treated with etoposide (20 μm) or DMSO for 48 h. After fixation, cells were stained with propidium iodide and their DNA content (FL3-H, log scale) was analyzed by flow cytometry as indicated in the supplemental Experimental Procedures. In each histogram, a black line demarks the sub-G1 cell population. E, Knockdown of FBXO3 attenuates etoposide-induced apoptosis. Percentage of apoptotic cells from B–D are presented as mean ± S.D. F, p53 levels increase after DNA damage. Cells generated as in B–D were treated with either etoposide (+) or DMSO (−) for 24 h. Total lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted as indicated. G, Proposed FBXO3-based mechanism for functional specification of mDia2's activity. Auto-inhibited mDia2 (closed conformation) can exist in an FBXO3-free (1) or an FBXO3-bound (2) state. In its FBXO3-bound state (2), mDia2 efficiently contributes to p53 regulation. Transition from the closed to the open conformation ((1) to (3) and (2) to (4)) unleashes mDia2's actin polymerization activity, which inhibits the activity of the mDia2-FBXO3 complex (4) on p53 (dashed red line).