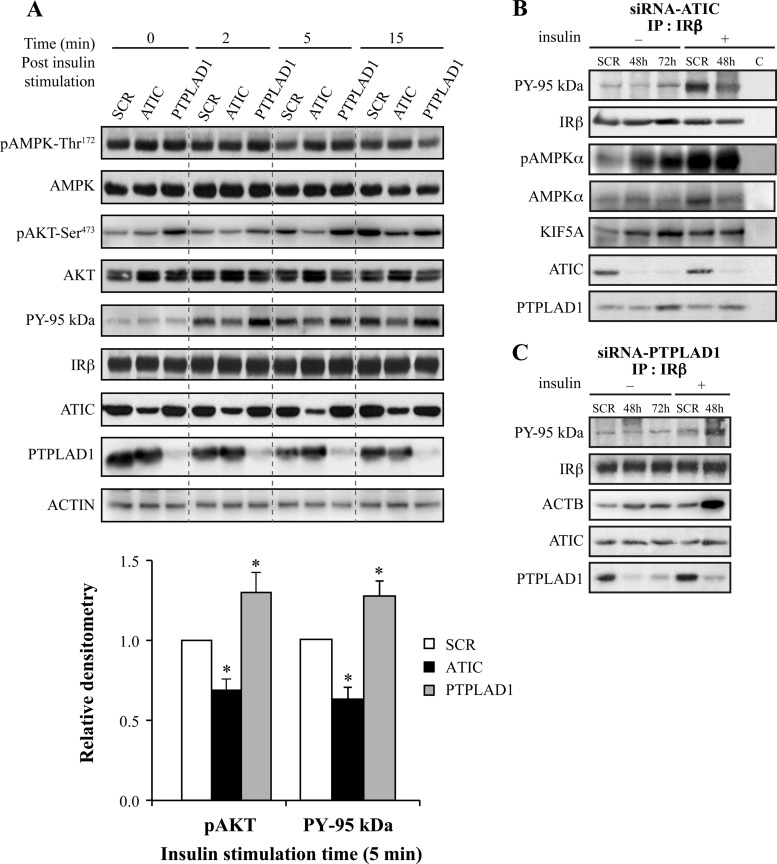
Fig. 4.
ATIC, PTPLAD1, and AMPK bind to IR in cultured cells. ATIC and PTPLAD1 knockdown affects the tyrosine phosphorylation of IR, and ATIC affects the phosphorylation of AMPK. A, HEK293 cells were transfected for 48 or 72 h with ATIC or PTPLAD1 siRNAs. The cells were preincubated in a serum-free medium for 2 h and stimulated for the indicated times with insulin (35 nm). Immunoblots (25 μg protein extracts) show the levels of IR, PY-95 kDa, PTPLAD1, ATIC, AMPK, pAMPK-Thr172, AKT, pAKT-Ser473, and actin in the cells that were transfected with control (SCR: scrambled 48 h), ATIC and PTPLAD1 siRNAs. The salient 5 min time point for pAKT-Ser473 and PY-95Kda (lower panel) is the mean ± s.d. of three experiments (*p < 0.01; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests). B, IR immunoprecipitation: After transfection with ATIC siRNA, the cells were incubated in serum-free medium for 2 h and stimulated for 15 min with vehicle (−) or insulin (+, 48 h post-transfection). The tyrosine phosphorylation of the IR β-subunit was measured using an antiphosphotyrosine (PY20) antibody. The presence of AMPK and pAMPK-Thr172 was verified using portions of the same membrane (three experiments). C, IR immunoprecipitations: After transfection with PTPLAD1 siRNA, the cells were incubated in serum-free medium for 2 h and stimulated for 15 min with vehicle (−) or insulin (+, 48 h post-transfection). The tyrosine phosphorylation of the IR β-subunit (PY 95 kDa) and the actin (ACTB) levels were measured using antibeta actin and PY20 antibodies (portions of the same membrane; three experiments).