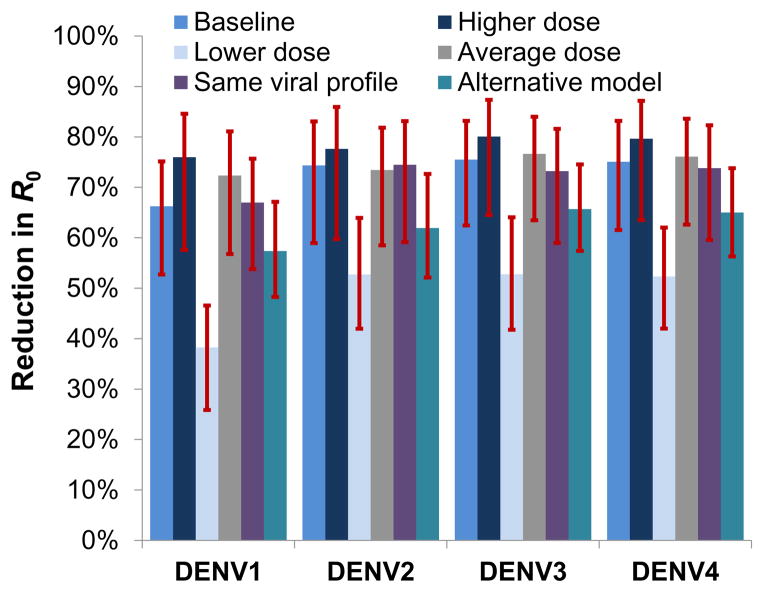
Figure 6.
Estimated reduction in transmissibility of DENV (quantified by serotype specific R0) caused by wMel infection. Median posterior estimates and 95% credible intervals are shown. ‘Baseline’ scenario: assumes data on infectious saliva translates directly to human infectiousness. ‘Higher/Lower dose’ scenarios: assume 10-fold higher/lower infectious dose for mosquito-to-human transmission than estimated using saliva infection model. ‘Average dose’: assumes same infectious dose for all serotypes (average across serotypes) for mosquito-to-human transmission. ‘Same viral profile’: uses a model of human viral kinetics that is the same for all serotypes. ‘Alternative model’: uses the alternative saliva infection model where wMel infection affects only the EIP.