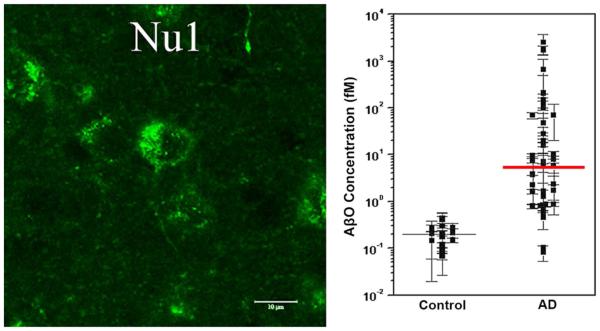
Fig. 4.
AβOs can accumulate in intracellular and extracellular pools. Intracellular AβOs are detectable in animal models overproducing APP and Aβ; however, the presence of extracellular AβOs on dendrites and in CSF suggests they are also important in AD. Left A representative micrograph of confocal fluorescence labeling of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ)-oligomer-specific antibody NU1 immunoreaction in young, pre-plaque Tg mice shows intracellular localization of AβOs. Adapted from Ferretti et al. [40]. Right A scatter plot from the ultrasensitive scanometric detection of AβOs in cerebrospinal fluid. Adapted from Georganopoulou et al. [45]. The response for the negative human control subject (brain extract) was similar to that observed for the chip control. The data points are averages of several separate experiments normalized for each assay based on the highest response in a series of runs. The mean values for ADDL concentrations (solid lines) are estimated for each group based on a calibration curve