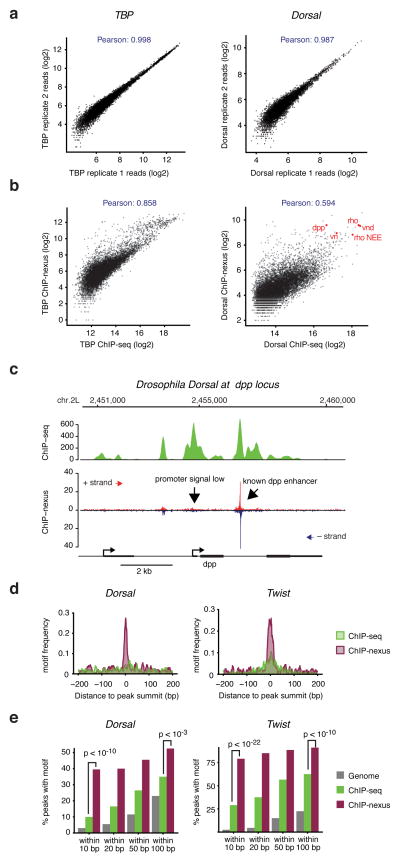
Figure 2. High reproducibility, resolution and specificity of ChIP-nexus as compared to ChIP-seq.
(a) Comparisons between biological ChIP-nexus replicates were performed by calling peaks using MACS 2 20 in replicate 1 (200 bp centered on the peak summit, up to 10,000 peaks as arbitrary cutoff) and by plotting the average raw reads for each peak in both replicates. A tight line is observed for all factors, corresponding to Pearson correlations of 0.98–0.99. TBP, which has the highest correlation, is shown on the left, whereas Dorsal, which has the lowest correlation, is shown on the right. (b) Comparison between ChIP-seq and ChIP-nexus. Peaks were called in the ChIP-seq data as in (a) and reads in these peaks from ChIP-seq and ChIP-nexus data are shown as a scatter plot. As can be seen for both TBP and Twist, there is an overall good correlation between the bulk data (Pearson correlations between 0.5–0.9). However, the ChIP-nexus data show an increased signal for a fraction of peaks. (c) Examination of individual examples shows that the ChIP-nexus signal is indeed highly specific. For example, the known dpp enhancer as shown in Figure 2 has a strong ChIP-nexus footprint (arrow), whereas the signal at the dpp promoter, which is equally high in the ChIP-seq data, has much lower and more distributed ChIP-nexus reads without any typical footprint (arrow). (d) Frequency distribution of consensus motifs in peaks identified by ChIP-seq (green) and ChIP-nexus (purple). Shown are the examples of Dorsal (left), for which ChIP-nexus shows a dramatic increase in motifs directly at the summit of the peaks, as well as for Twist (right), for which ChIP-nexus shows a more moderate improvement in motif frequency over ChIP-seq. (e) Quantification of the motif frequency in random genomic regions, in ChIP-seq peaks and in ChIP-nexus peaks within increasing windows from the peaks’ summits for Dorsal and Twist. ChIP-nexus performs much better at a close interval to the peak summit (within 10 bp on either side, Chi2 test, Dorsal p<10−11, Twist p<10−14), underscoring the increased specificity of ChIP-nexus. But even at wider intervals (within 100 bp on either side of the summit), ChIP-nexus peaks contain more motifs (Chi2 test, Dorsal p<2×10−3, Twist p<10−5), suggesting that ChIP-nexus has higher specificity as compared to ChIP-seq.