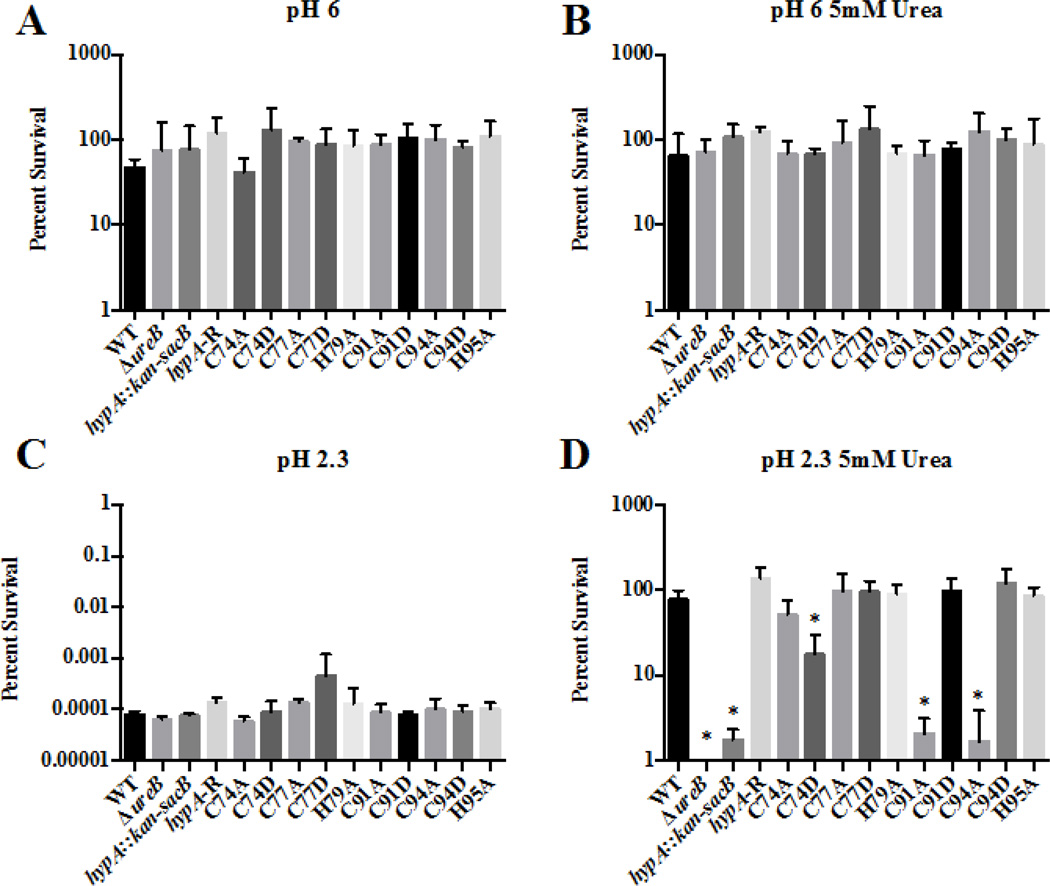
Fig. 2.
Specific amino acid mutations within the zinc-binding site of the HypA protein in Helicobacter pylori result in decreased acid resistance. The ten hypA mutants, as well as the wild type (WT), ureB knockout (ΔureB), hypA interrupted mutant (hypA::kan-sacB), and the hypA-restorant (hypA-R) were exposed to various environments for 1 hour: pH 6 (A), pH 6 containing 5mM urea (B), pH 2.3 (C), and pH 2.3 containing 5mM urea. Percent survival was calculated for each strain. Data represent mean ± standard deviation. * = Acid resistance was significantly reduced when compared to wild type (p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons).