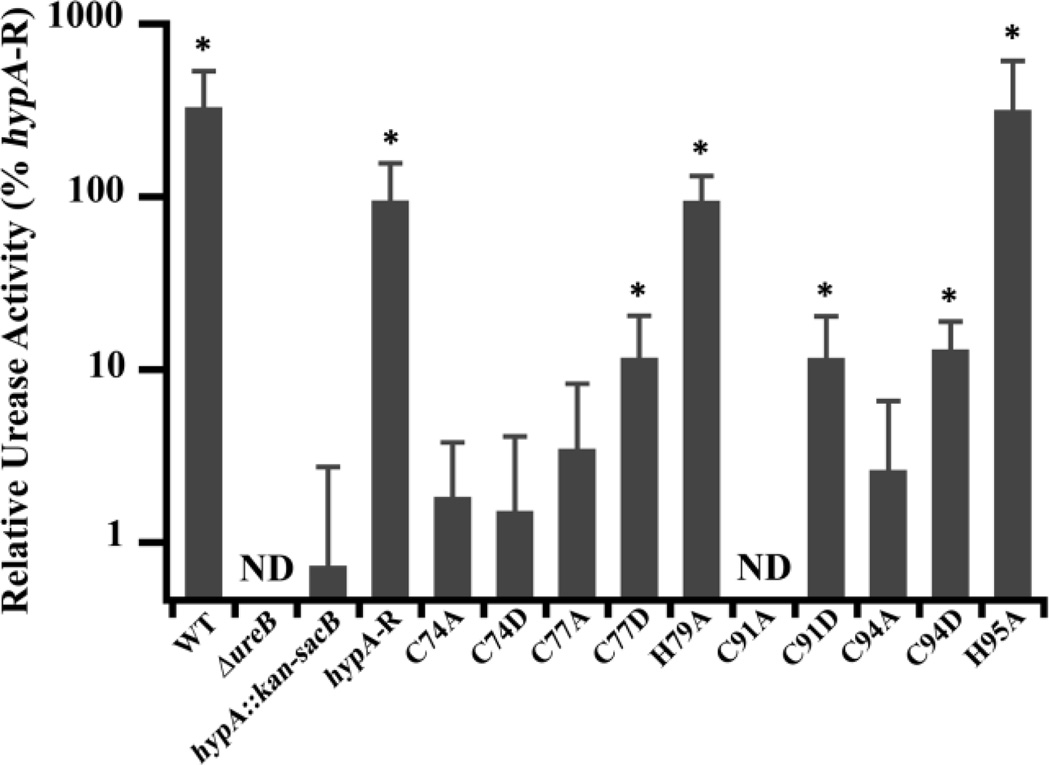
Fig. 3.
Zn-site mutations of hypA in H. pylori lead to deficiencies in urease activity. Soluble whole cell extracts were obtained from lysis of ten hypA Zn-site mutant strains, as well as the wild type (WT), ureB knockout (ΔureB), hypA interrupted mutant (hypA::kan-sacB), and the hypA-restorant (hypA-R) strains. The phenol-hypochlorite method was used to assay the ammonia production (urease activity) of the strains. Amount of ammonia produced was quantified by comparison with a standard curve constructed with known amount of ammonium chloride. The ΔureB strain activity was subtracted from each strain as background ammonia in cell extracts and all activity was normalized to hypA-R strain. * = Urease activity was significantly different from the hypA::kan-sacB strain (p < 0.05). ND = none detected.