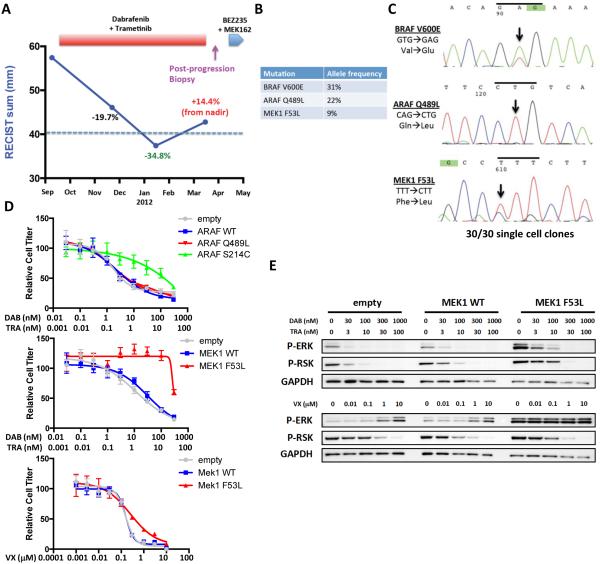
Figure 4. MEK1 F53L mutation drives clinical acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition.
(A) Clinical time course of therapy for BRAF-mutant CRC patient #3 showing dates of therapy and timing of post-progression biopsy. Cumulative tumor diameter as measured by RECIST is shown throughout the treatment course. (B) List of key mutations identified in the post-progression biopsy with associated allele frequencies. (C) Sanger sequencing of a patient-derived cell line generated from the post-progression biopsy for BRAF V600E, ARAF Q489L, and MEK1 F53L. All mutations were found to be present in 30 of 30 single cell clones. (D) Cells expressing the indicated constructs were treated with dabrafenib plus trametinib or VX-11e as shown for 72h, and relative cell titer was determined. (E) Cells expressing wild-type MEK1 (MEK1 WT), MEK1 F53L, or empty vector control were treated with the indicated concentrations of drugs for 24h, and western blotting was performed with the indicated antibodies.