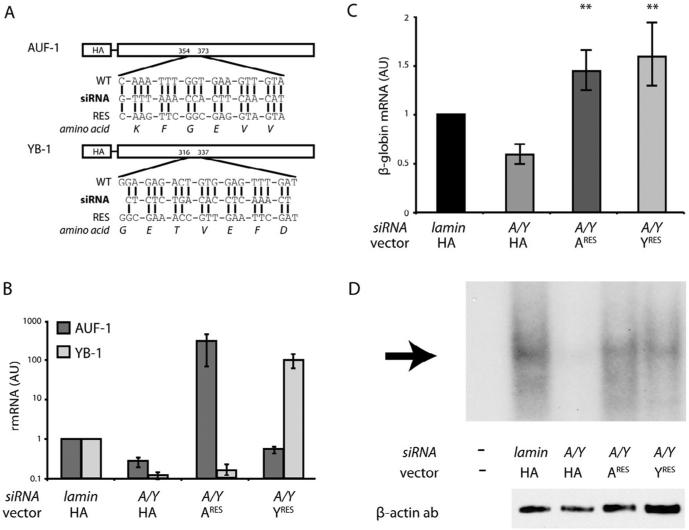
Fig. 3.
Rescue expression of either AUF-1 or YB-1 independently restores β-globin mRNA to normal levels. (A) Sequence comparison of endogenous and siRNA-resistant HA-AUF-1 and HA-YB-1. For each factor, the siRNA sequence (bold), the endogenous mRNA target sequence (WT), the siRNA-resistant sequence (RES), and the translated amino-acid sequence are illustrated. Vertical lines indicate nucleotide identity. Numbers indicate the position of each sequence in the respective ORF. (B) Levels of siRNA-resistant HA-AUF-1 or HA-YB-1 mRNAs in siRNA-transfected and control cells. K562 cells were co-transfected with siRNAs targeting AUF-1 (A) and YB-1 (Y), along with rescue vectors encoding either siRNA-resistant HA-AUF-1 mRNA (ARES) or siRNA-resistant HA-YB-1 mRNA (YRES). AUF-1 and YB-1 mRNAs were quantified by RT-qPCR and normalized to average levels of control GAPDH and β-actin mRNAs. As a negative control, a vector encoding parental HA mRNA was co-transfected with an siRNA targeting lamin mRNA. Levels of AUF-1 and YB-1 in lamin siRNA-transfected cells were assigned unit value. Each bar represents the mean±SEM values for 5 experimental replicates. Note logarithmic ordinate scale. (C) Rescue of β-globin mRNA levels by siRNA-resistant HA-AUF-1 and siRNA-HA-YB-1. For experimental set-up, see panel B. Each bar represents the mean±SEM values for experimental replicates. **p < 0.01 compared to A/Y siRNA/HA-construct (one-tailed). (D) Reconstitution of the β-complex in AUF-1-rescued or YB-1-rescued K562 cells. Top: R-EMSA analyses were conducted on a [32P]-labeled RNA corresponding to the β-globin 3′UTR, using cytoplasmic extracts from AUF-1-depleted and/or YB-1-depleted cells, or from similar cells expressing siRNA-resistant HA-AUF-1 or HA-YB-1. Arrow indicates the β-complex. Bottom: Western-transfer analyses of the same extracts, using a β-actin antibody.