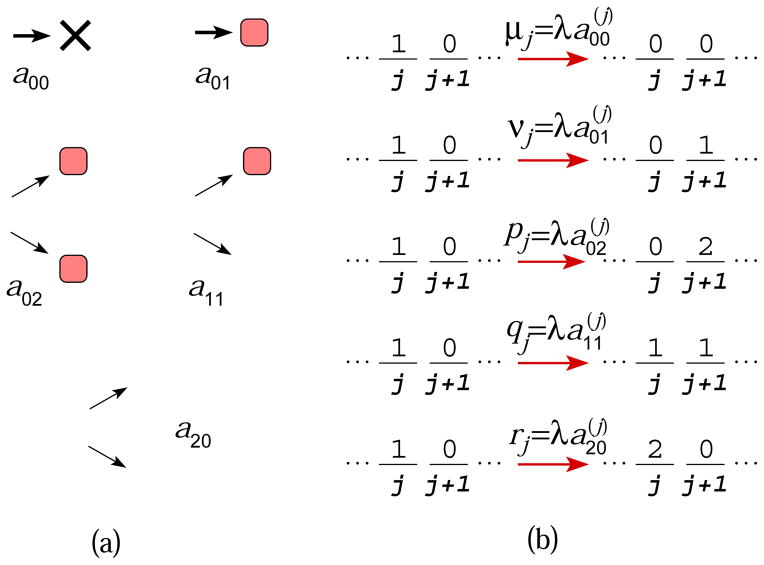
Figure 2.
(a) The five possible transitions of a single cell at an initial stage (white) and their probabilities amn. Dividing cells can produce daughters at a more differentiated or mutated stage (red). Since these are the only possible steps, a00 + a01 + a11 + a20 + a02 = 1. (b) When inter-transition times are exponentially distributed, the rates of each process can be defined in terms of the branching rate and the branching probabilities at each node k.