Table 2. Comparisions of the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its components among three antipsychotic groups with different metabolic side effects.
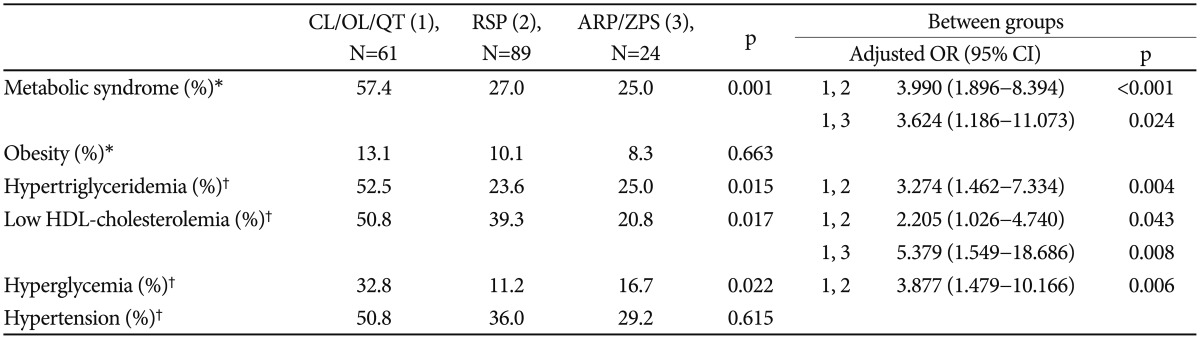
Obesity, BMI ≥30 kg/m2; Hypertriglyceridemia, fasting plasma triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL; low HDL-cholesterolemia, HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL in male, <50 mg/dL in female; hyperglycemia, fating plasma glucose ≥100 mg/dL; hypertention, systolic BP ≥130 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥85 mm Hg. *data are adjusted for differences in age, sex, duration of current AAPs, and HPD-equivalent dosage of current AAP, †data are adjusted for differences in age, sex, BMI, duration of current AAP, and HPD-equivalent dosage of current AAP. CL: clozapine, OL: olanzapine, QT: quetiapine, RSP: risperidone, ARP: aripiprazole, ZPS: ziprasidone, BMI: body mass index, HDL: high density lipoprotein, BP: blood pressure, AAP: atypical antipsychotic, HPD: haloperidol
