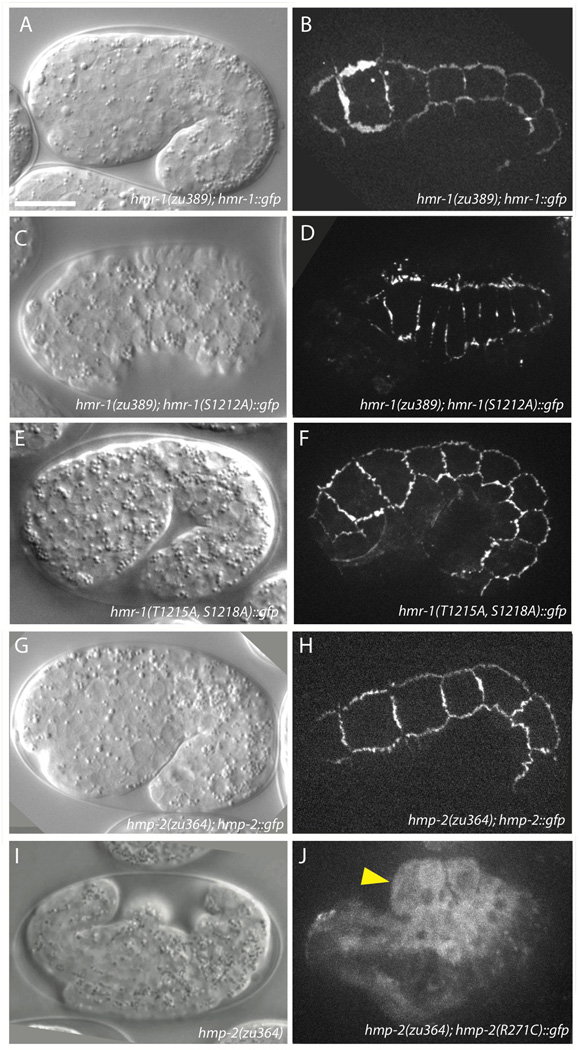
Figure 5. HMR-1 pS1212 is required for interaction between HMP-2 and HMR-1.
(A, B) DIC (A) and confocal (B) images of 1.5-fold elongating hmr-1(zu389) homozygotes rescued to viability by HMR-1::GFP. Lethality in offspring of hmr-1(zu389); hmr-1::gfp mothers is 85.2% (n = 209). Signal localizes to epidermal adherens junctions similarly to HMR-1 immunostaining (not shown). Scale bar is 10 µm.
(C, D) The phospho-null construct HMR-1(S1212A)::GFP localizes to junctions but is unable to rescue hmr-1(zu389) homozygotes to viability. Lethality in offspring of hmr-1(zu389)/+; hmr-1(S1212A)::gfp mothers is 27.4% (n = 1072). Cells in (D) appear compressed due to retraction of the hypodermis subsequent to failure of epiboly.
(E, F) HMR-1(T1215A, S1218A)::GFP localizes to junctions and rescues hmr-1(zu389) embryonic enclosure and elongation. The hmr-1 transgene reduces embryonic lethality of hmr-1(zu389)/+ offspring from 24.9% (n=1101) to 16.9% (n=1055, 3 independent lines). Pictured is a representative offspring from a hmr-1(zu389)/+; hmr-1(T1215A, S1218A)::gfp mother.
(G, H) Wildtype HMP-2::GFP localizes to junctions (H) and rescues hmp-2(zu364) to viability (G).
(I) hmp-2(zu364) homozygotes fail to elongate and die with the Humpback phenotype. The zu364 lesion was identified as a point mutation resulting in HMP-2 R271C.
(J) HMP-2(R271C)::GFP localizes exclusively to the cytoplasm, and embryos die with the Hmp phenotype, consistent with a model in which this residue is crucial for interacting with HMR-1 pS1212. Arrowhead indicates dorsal humps.