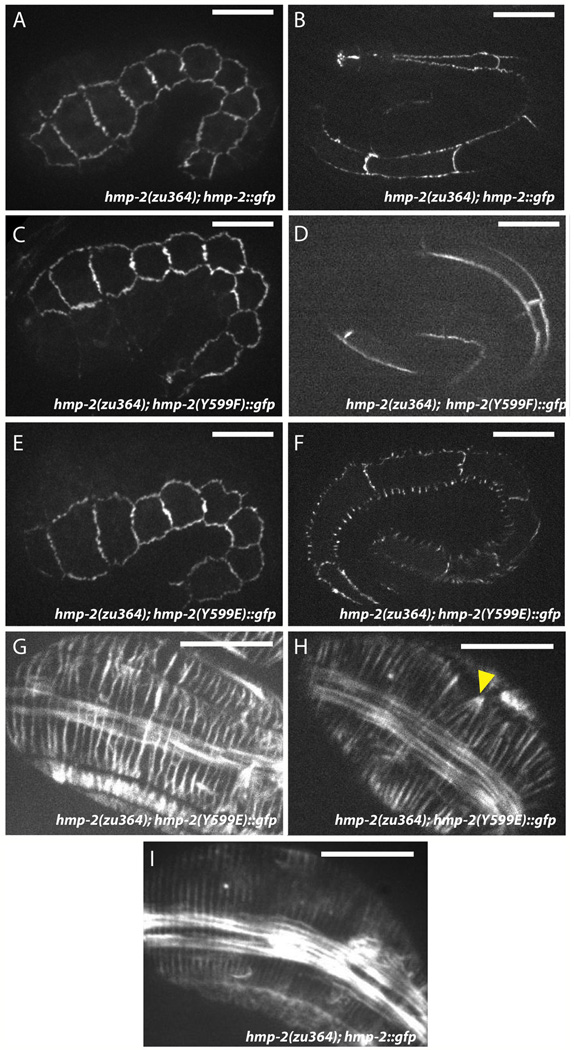
Fig 6. HMP-2 Y599E localizes aberrantly and produces mild circumferential F-actin bundle (CFB) defects.
(A,B) Wildtype HMP-2::GFP signal is well established by early elongation (A) and is maintained at junctions through late elongation (B). Rescued zu364 homozygotes display 53.9% lethality (n = 178), approximately commensurate with the transmission rate of the extrachromosomal array carrying the transgene. Scale bar is 10 µm.
(C,D) HMP-2(Y599F)::GFP rescues hmp-2(zu364) homozygotes and localizes to epidermal adherens junctions identically to wildtype HMP-2::GFP both in early (C) and late (D) elongation. Rescued zu364 homozygotes display 50.2% lethality (n = 305).
(E,F) HMP-2::GFP Y599E rescues hmp-2(zu364). Signal initially localizes to adherens junctions (E), but it becomes punctate during late elongation, and fluorescent excursions form orthogonally to junctions between lateral (seam) cells and their dorsal and ventral neighbors (F). Rescued zu364 homozygotes display 45.9% lethality (n = 283).
(G–I) CFBs visualized by phalloidin staining in hmp-2(zu364) homozygotes rescued by wildtype (I) or Y599E (G, H) HMP-2::GFP constructs. Wildtype HMP-2::GFP embryos display evenly-distributed radial F-actin bundles (I). CFBs in Y599E embryos become irregularly spaced (G, H), and occasionally multiple bundles aggregate to a single locus on the junction (H, arrowhead). Scale bar is 10 µm.